PowerPC™ 405 Processor Block Reference Guide www.xilinx.com 97
UG018 (v2.0) August 20, 2004 1-800-255-7778
R
DSPLB Aborted Data-Access Request
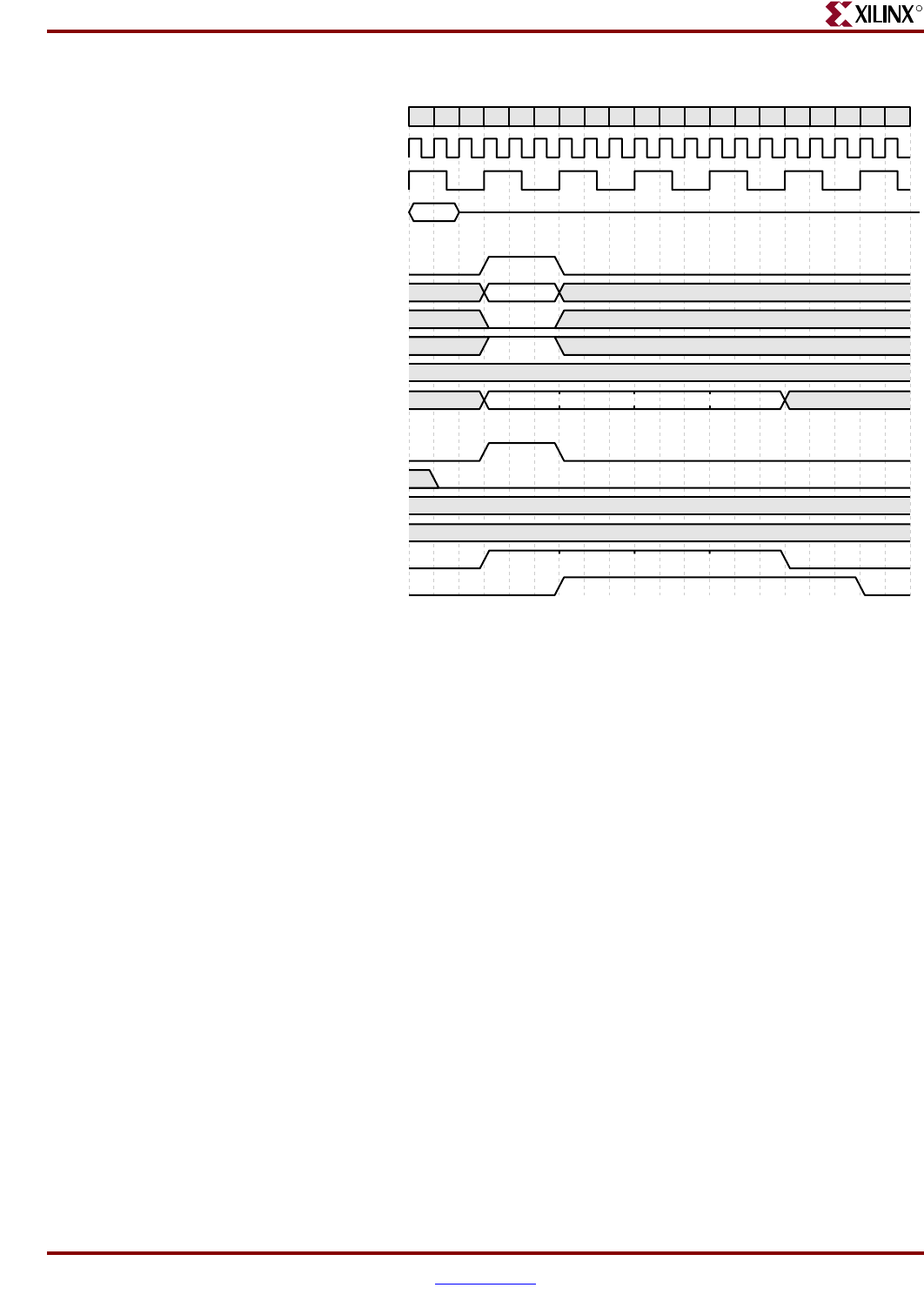
The timing diagram in Figure 2-28 shows an aborted data-access request. The request is
aborted because of a core reset. The BIU is not reset.
A line write (wl1) is requested by the DCU in cycle 3 in response to a cache flush
(represented by the flush1 transaction in cycles 1 through 2). The BIU responds in the same
cycle the request is made by the DCU. Data is sent from the DCU to the BIU in cycles 3
through 6.
A line read (rl2) is address pipelined with the previous line write. The rl2 request is made
by the DCU in cycle 5 and the BIU responds in the same cycle. However, the processor also
aborts the request in cycle 5. Therefore, no data is transferred from the BIU to the DCU in
response to this request.
Because the BIU is not reset, it must complete the first line write even though the processor
asserts the PLB abort signal during the line write.
Figure 2-27: DSPLB 3:1 Core-to-PLB Line Write
Cy cle
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
CPMC405CLK
UG018_31_101701
PPC405 Outputs:
C405PLBDCUREQUEST
C405PLBDCURNW
C405PLBDCUABUS[0:31]
adr1
flush1
C405PLBDCUBE[0:7]
C405PLBDCUWRDBUS[0:63]
C405PLBDCUSIZE2
DCU
wl1
d1
01
d1
23
d1
45
d1
67
PLBCLK
PLB/BIU Outputs:
PLBC405DCUADDRACK
PLBC405DCURDDBUS[0:63]
PLBC405DCURDWDADDR[1:3]
PLBC405DCURDDACK
PLBC405DCUWRDACK
PLBC405DCUBUSY
wl1
wl1
01
wl1
23
wl1
45
wl1
67


















