178 www.xilinx.com PowerPC™ 405 Processor Block Reference Guide
1-800-255-7778 UG018 (v2.0) August 20, 2004
Chapter 3: PowerPC 405 OCM Controller
R
DSOCM Data Load, Variable Latency
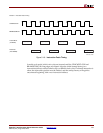
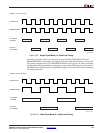
Figure 3-26 and Figure 3-27 show two load operations with variable latency for single cycle
mode and multi-cycle mode with a CPMC405CLOCK:BRAMDSOCMCLK ratio of 2:1.
In both single-cycle mode and multi-cycle mode, the data load operation consists of the
following sequence:
1. The CPU launches the load request to the OCM controller.
2. The OCM controller translates the CPU order, routes the address, and asserts all of the
necessary control signals.
Note: Read control signals (DSOCMBRAMEN, DSOCMRDADDRVALID) are active for only
one BRAMDSOCMCLK cycle and must be registered in the FPGA fabric if they are required for
further processing.
Note: DSOCMRDADDRVALID indicates a valid read address on the DSOCMRDABUS.
DSOCMBRAMEN is also asserted for both read or write requests. However, one can choose to
ignore this signal if the design does not use BRAMs.
3. The slave waits for multiple BRAMDSOCMCLK cycles–the number of clock cycles
depends on the application–and then asserts DSOCMRWCOMPLETE, which must be
accompanied by valid read data.
4. The DSOCM controller sees the completion signal (DSOCMRWCOMPLETE) and
latches the read data driven by the slave on BRAMDSOCMRDDBUS.
5. The DSOCM controller forwards the data back to the PPC405.
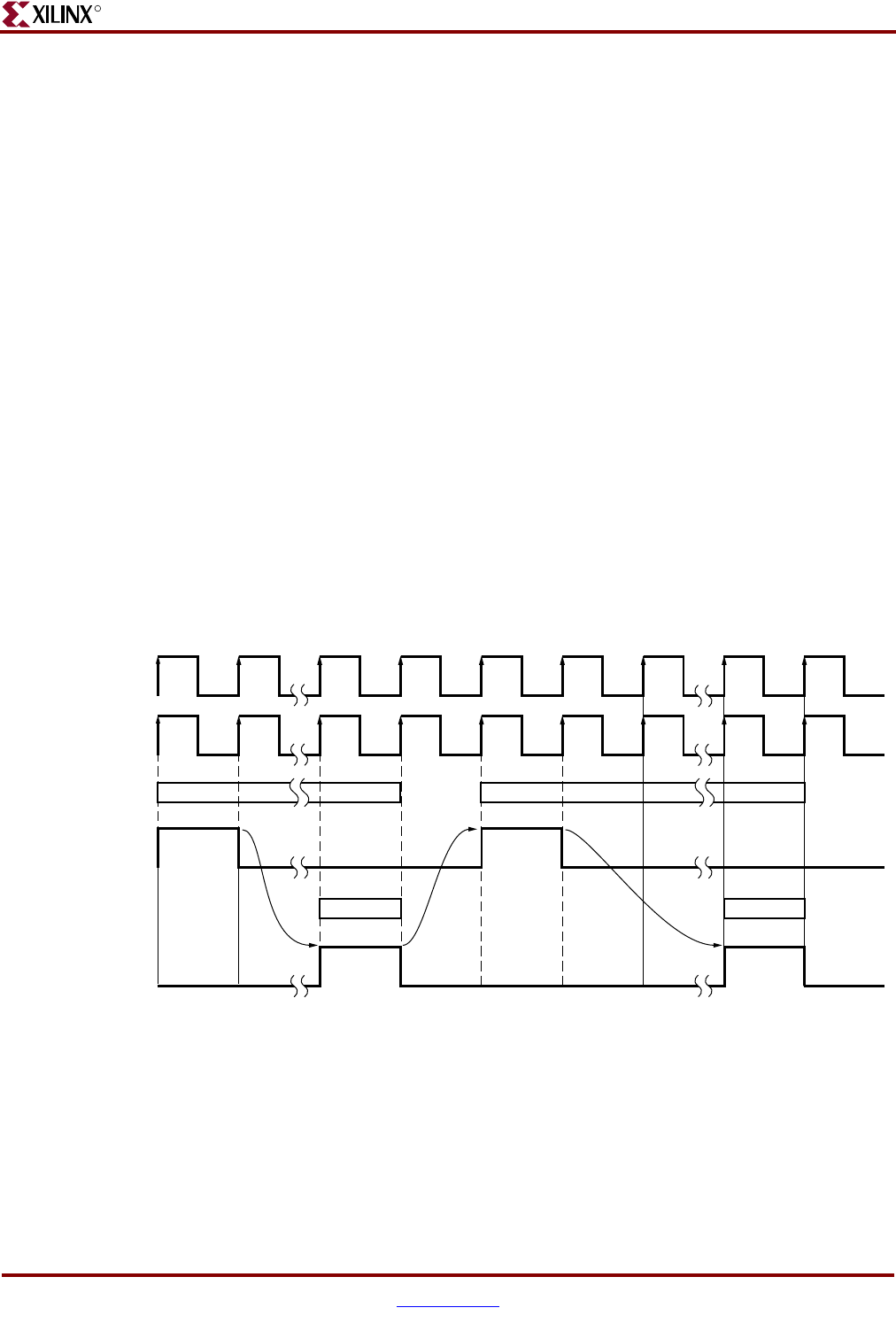
Figure 3-26: Single Cycle Mode (1:1) DSOCM Read Variable Latency for Virtex-4
UG018_62c_11210
3
C
PMC405Clock
D
SOCM 1:1 Data Load Timing (Variable latency, DSOCMRDWRCOMPLETE driven by OCM slaves)
B
RAMDSOCMCLK
L_addr_1 L_addr_2
Rd_data_1 Rd_data_2
Read addr
valid
next valid
B
oth DSOCMBRAMEN and
D
SOCMRDADDRVALID
a
s rd addr valid
(
To BRAM or Slave)
R
ead Complete
(
From BRAM or Slave)
L
oad Address
(
To BRAM or Slave)
R
ead Data
(
From BRAM or Slave)
complete complete