1-21
Introduction
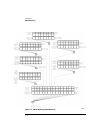
Status Reporting
enabled conditions in the Jitter Event Register has occurred. You can mask the EFAIL,
JLOSS, and AREQD bits, thus preventing them from setting the JIT bit, by setting corre-
sponding bits to zero using the JEE command. Refer to “JEE” on page 4-7.
Mask Test Event
Register (MTER)
Bit 0 (COMP) of the Mask Test Event Register is set when the Mask Test completes. The
Mask Test completion criteria are set by the MTESt:RUNTil command. Refer to “RUNTil” on
page 17-6. Bit 1 (FAIL) of the Mask Test Event Register is set when the Mask Test fails. This
will occur whenever any sample is recorded within any region defined in the mask. The Mask
Test Event Register is read and cleared with the MTER? query. Refer to “MTER?” on
page 4-10. When either the COMP or FAIL bits are set, they in turn set the MTEST bit (bit
10) of the Operation Status Register. You can mask the COMP and FAIL bits, thus preventing
them from setting the MTEST bit, by setting corresponding bits to zero using the MTEE com-
mand. Refer to “MTEE” on page 4-10.
Precision
Timebase Event
Register (PTER)
The Precision Timebase feature requires the installation of the Agilent 86107A Precision
Timebase Module. Bit 0 (LOSS) of the Precision Timebase Event Register is set when loss of
the time reference occurs. Time reference is lost when a change in the amplitude or fre-
quency of the reference clock signal is detected. The Precision Timebase Event Register is
read and cleared with the PTER? query. Refer to “PTER?” on page 4-12. When the LOSS bit is
set, it in turn sets the PTIME bit (bit 11) of the Operation Status Register. Results from the
Precision Timebase Register can be masked by using the PTEE command to set the Precision
Timebase Event Enable Register to the value 0. You enable the LOSS bit by setting the mask
value to 1. Refer to “PTEE” on page 4-11.
Error Queue As errors are detected, they are placed in an error queue. This queue is first in, first out. If
the error queue overflows, the last error in the queue is replaced with error –350, “Queue
overflow”. Any time the queue overflows, the oldest errors remain in the queue, and the most
recent error is discarded. The length of the instrument's error queue is 30 (29 positions for
the error messages, and 1 position for the “Queue overflow” message). The error queue is
read with the SYSTEM:ERROR? query. Executing this query reads and removes the oldest
error from the head of the queue, which opens a position at the tail of the queue for a new
error. When all the errors have been read from the queue, subsequent error queries return 0,
“No error.” The error queue is cleared when any of the following occurs:
• When the instrument is powered up.
• When the instrument receives the *CLS common command.
• When the last item is read from the error queue.
For more information on reading the error queue, refer to the SYSTEM:ERROR? query in
Chapter 5, “System Commands”. For a complete list of error messages, refer to “Error Mes-
sages” on page 1-46.