Groundsmaster 5900/5910 Hydraulic SystemPage 4 -- 29
Engine Cooling Fan Circuit
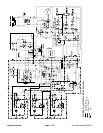
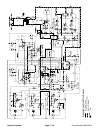
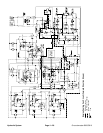
A three section gear pump is coupled to the piston (trac-
tion) pump. The gear pump section (P3) farthest from
the piston pump supplies hydraulic flow to the steering/
cooling fan control manifold, the lift control manifold and
the traction charge circuit. Hydraulic flow from pump
section (P3) is split between the steering/cooling fan/
charge circuit and the lift/lower circuit by a proportional
flow divider located in the lift control manifold. This flow
divider splits pump flow approximately 75% for the
steering/cooling fan/charge circuit (10.5 GPM/39.7
LPM) and 25% for the lift/lower circuit (3.5 GPM/13.2
LPM).
The steering/cooling fan control manifold controls the
operation of the steering control valve and the gear mo-
tor that drives the engine cooling fan. Priority valve (PV)
in the manifold controls the oil flow to the steeringcontrol
valve which is a closed center, load sensing valve. The
steering control valve senses the oil flow that is needed
for steering and the priority valve (PV) will supply the
correct amount. Oil not used by steering is provided to
the fan motor. The steering/cooling fan control manifold
controls the speed and direction of the fan motor based
on electrical output from the TEC--5002 controller.
With the steering wheel in the neutral, at rest position
and the engine running, hydraulic oil from the lift control
manifold flow divider enters the steering/cooling fan
control manifold port P, flows through the priority valve
(PV) and to the steering control valve where it dead
heads at the spool. Oil is also sent to both ends of the
(PV) spool. On one end of the spool, oil is directed to the
steering relief valve (RV) and also is directed through
the OR orifice and out the LS manifold port to the steer-
ing control valve. This flow provides steering load sense
pressure and is directed through a small passage in the
steering control valve spool and sleeve before returning
to the charge circuit. While this load sense pressure is
returning to the charge circuit, the priority valve (PV)
spool shifts to direct pump flow to the cooling fan motor
circuit. Without steering input, no oil is flowing through
the steering control valve so all circuit oil is available for
thecoolingfanmotor.
Oil flow from the priority valve (PV) to the cooling fan is
controlled by the proportional relief valve (PRV). The
(PRV) adjusts fan circuit pressure and flow based on a
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal from the
TEC--5002 controller. The controller uses engine cool-
ant and hydraulic oil temperatures to determine the
proper PWM signal for the (PRV) valve. The fan circuit
flow determines the speed of the cooling fan.
If the fan motor is stalled for any reason, the priority
valve (PRV) has a secondary function as a circuit relief
to limit fan motor pressure to 3300 PSI (228 bar).
When the engine is shut off, the over--running inertia
load of the fan blades keeps driving the fan motor and
turns it into a pump. The check valve (CV) in the steer-
ing/cooling fan control manifold will open to keep the
motor circuit full of oil so the fan motor will not cavitate.
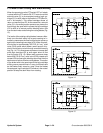
Forward Direction Fan Operation
Oil flow from the priority valve (PV) is sent through the
de--energized solenoid valve (S), out manifold port M1
and then to rotate the cooling fan motor. Return flow
from the motor enters the manifold at port M2, through
the de--energized solenoid valve (S), out manifold port
CH and is then used for traction circuit charge oil.
Reverse Direction Fan Operation
The TEC--5002 controller can reverse the cooling fan to
clean debris from the radiator, oil cooler and rear intake
screen. If hydraulic oil and/or engine coolant tempera-
tures increase to an unsuitable level, the PWM signal to
the (PRV) valve is sent to slow the cooling fan. The con-
troller then energizes solenoid valve (S) in the steering/
cooling fan control manifoldto reversecooling fan motor
oil flow so that it runs in the reverse direction. The con-
troller determines the length of time that the fan should
be run in reverse before fan rotation is returned to the
forward direction.
Hydraulic
System