2-8 PXA250 and PXA210 Applications Processors Design Guide
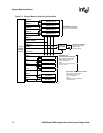
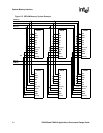
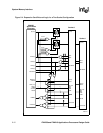
System Memory Interface
Memory types are programmable through the memory interface configuration registers.
Six chip selects control the static memory interface, nCS<5:0>. All are configurable for nonburst
ROM or Flash memory, burst ROM or Flash, SRAM, or SRAM-like variable latency I/O devices.
The variable latency I/O interface differs from SRAM in that it allows the data ready input signal
(RDY) to insert a variable number of memory-cycle-wait states. The data bus width for each chip
select region may be programmed to be 16-bit or 32-bit. nCS<3:0> are also configurable for
Synchronous Static Memory.
For SRAM and variable latency I/O implementations, DQM<3:0> signals are used for the write
byte enables, where DQM<3> corresponds to the MSB. The applications processor supplies 26-
bits of byte address for access of up to 64 Mbytes per chip select. However, when the address is
sent out on the MA pins, MA reflects the actual address, not the byte address. The lower one or two
internal address bits are truncated appropriately.
2.6.2 Boot Time Defaults
Booting configuration is device specific. For example, you cannot use a 32-bit memory booting
configuration with a PXA210 applications processor. Table 2-5 shows valid booting configurations
based on processor type, while Table 2-6 shows boot selection definitions. See Section 7.10.2,
“Boot-Time Configurations” in the Intel® PXA250 and PXA210 Applications Processors
Developer’s Manual for more detailed descriptions of these Boot Time Configurations.
Table 2-5. Valid Booting Configurations Based on Package Type
Processor Type Valid Booting Configurations
0 (PXA210
applications
processor)
001
101
111
1 (PXA250
applications
processor)
000
001
100
101
110
111
Table 2-6. BOOT_SEL Definitions (Sheet 1 of 2)
BOOT_SEL
Boot From . . .
210
0 0 0 Asynchronous 32-bit ROM
0 0 1 Asynchronous 16-bit ROM
100
1 32-bit Synchronous Mask ROM (64 Mbits)
2 16-bit Synchronous Mask ROMs = 32-bits (32 Mbits each)