Rev. E
Groundsmaster 4000−D Page 6 − 27 Axles, Planetaries, and Brakes (Rev. B)
Pinion Gear to Ring Gear Engagement (4 Wheel Drive Axle)
The final position of the pinion gear is verified by using
the gear contact pattern method as described in the fol-
lowing procedure.
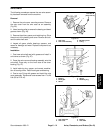
GEAR TOOTH DEFINITIONS (Fig. 39):
Toe − the portion of the tooth surface at the end to-
wards the center.
Heel − the portion of the gear tooth at the outer end.
Top Land − top surface of tooth.
1. Paint the teeth of the ring gear, both drive and coast
side, with a gear marking compound, such as DyKemR
Steel Blue.
2. Install the input shaft/pinion gear assembly into axle
case.
3. While applying a light load to the ring gear, rotate the
pinion gear in the direction of forward travel until the ring
gear has made one complete revolution.
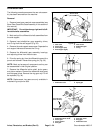
Ideal tooth contact observed on the ring gear should
cover more than 35% of each tooth surface. The contact
area should be in the center of each tooth and extend 1/3
to 1/2 way across each tooth from the toe end (Fig. 40).
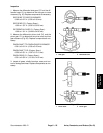
Adjustments to the gear contact position are made by
moving the input shaft/pinion gear (bearing case shims)
or by moving the differential gear case (differential bear-
ing shims) (Fig. 41).
NOTE: Bearing case shims are available in 0.004 in.
(0.10 mm) and 0.008 in. (0.20 mm) thickness.
NOTE: Differential bearing shims are available in
0.004 in. (0.10 mm), 0.008 in. (0.20 mm) and 0.016 in.
(0.40 mm) thickness.
Study the different contact patterns (Figs. 42 and 43)
and correct gear engagement as necessary.
NOTE: When making changes, note that two variables
are involved (see Gear Pattern Movement Summary in
this section of this manual).
Example: If the pinion gear to ring gear backlash is set
correctly to specifications and the bearing case shim is
changed to adjust tooth contact, it may be necessary to
readjust backlash to the correct specification before
checking the contact pattern.
Figure 39
TOE
HEEL
PROFILE
TOP LAND
ROOT
LENGTHWISE
BEARING
ARC
Figure 40
More than 35% total tooth contact
1/3 to 1/2 of entire width
from small end of tooth
1. Input shaft/pinion gear
2. Bearing case shims
3. Differential gear case
4. Differential bearing
shims
Figure 41
1
2
3
4
Axles, Planetaries,
and Brakes