170 Command-line switches
Clone switch usage
The number of size switches depends on the number of partition sizes that you
want to specify. There may be none.
SZE{E | F | L | n={xxxxM | mmP| F | V}}
Examples of clone switch usage
Table A-6 describes clone switches and their functions.
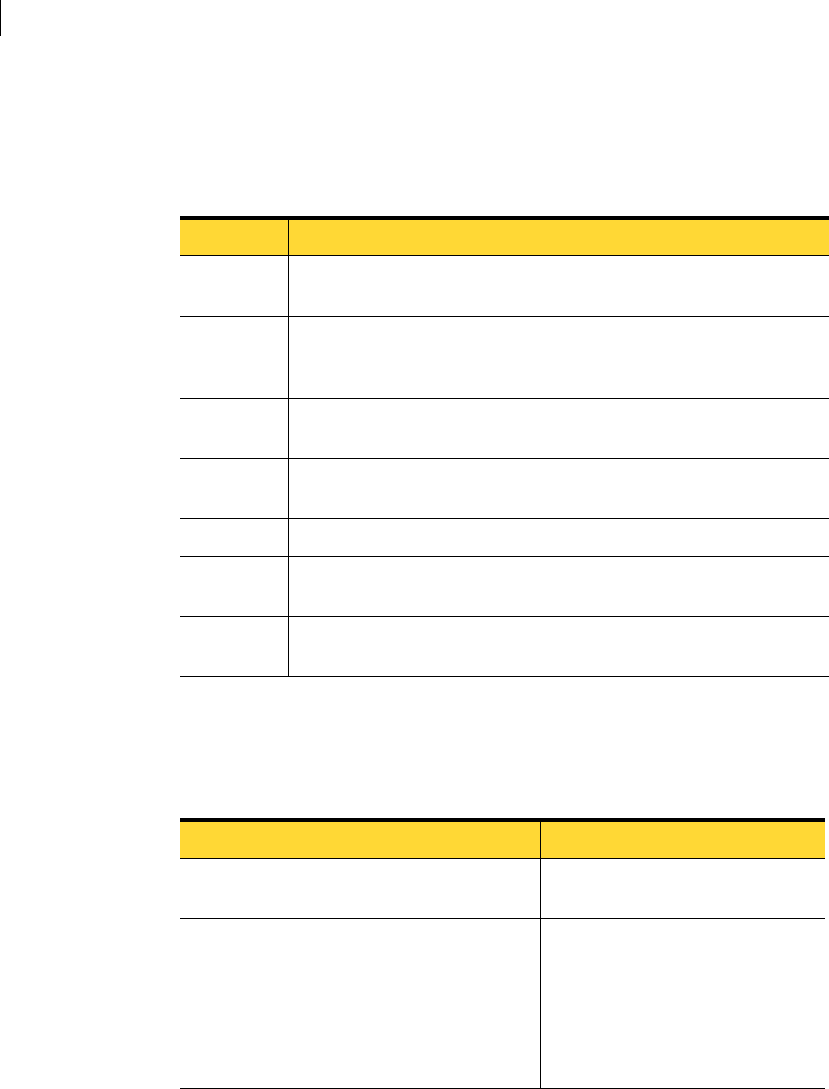
Table A-5 Destination size options for cloning
Switch Explanation
n=xxxxM Indicates that the nth destination partition is to have a size of xxxxMB
(for example, SZE2=800M indicates partition two is to have 800 MB).
n=mmP Indicates that the nth destination partition is to have a size of mm percent
of the target disk. Due to partition size rounding and alignment issues,
100% physical use of disk space may not be possible.
n=F Indicates that the nth destination partition is to remain the same size on
the destination as it was on the source. This is referred to as fixed size.
n=V Indicates that the partition may be made bigger or smaller depending on
how much disk space is available. This is the default.
E The sizes of all partitions remain fixed.
F The sizes of all partitions except the first remain fixed. The first partition
uses the remaining space.
L The sizes of all partitions except the last remain fixed. The last partition
uses the remaining space.
Table A-6 Clone switch usage examples
Switch Function
ghost.exe -clone,mode=copy,src=1,dst=2 Copies local disk one to local disk
two.
ghost.exe -lpm -clone,mode=create,src=2,dst=
c:\drive2.gho
Connects a master computer using
LPT to another computer running
Norton Ghost in slave mode, and save
a disk image of local disk two to the
remote file c:\drive2.gho. The slave
computer can be started with
ghost.exe -lps.


















