124 Using Ghost Explorer to modify image file contents
Using Ghost Explorer from the command line
If Ghost Explorer reports a corruption in your image file, you may be able to get
further details of the nature of the corruption. Normally, you would only use
these options when asked to do so by Ghost Explorer Technical Support.
Table 9-1 lists the arguments with which you can start the program.
The reports are presented to you as dialog boxes. You can use all switches or use
-d7 to turn on all options.
Ghost Explorer has a batch mode in which it carries out a single command and
then exits. In this version, batch mode supports the saving of the contents to a
text file only. To use this mode, specify one of the switches in Table 9-2.
See “Listing the contents of an image file” on page 121.
If Ghost Explorer reports that a spanned or split image is corrupt without
prompting for the second part of the image, it may not recognize that the image is
split. Starting with the -split argument forces Ghost Explorer to treat an image as
a split image.
See “Setting span file sizes” on page 121.
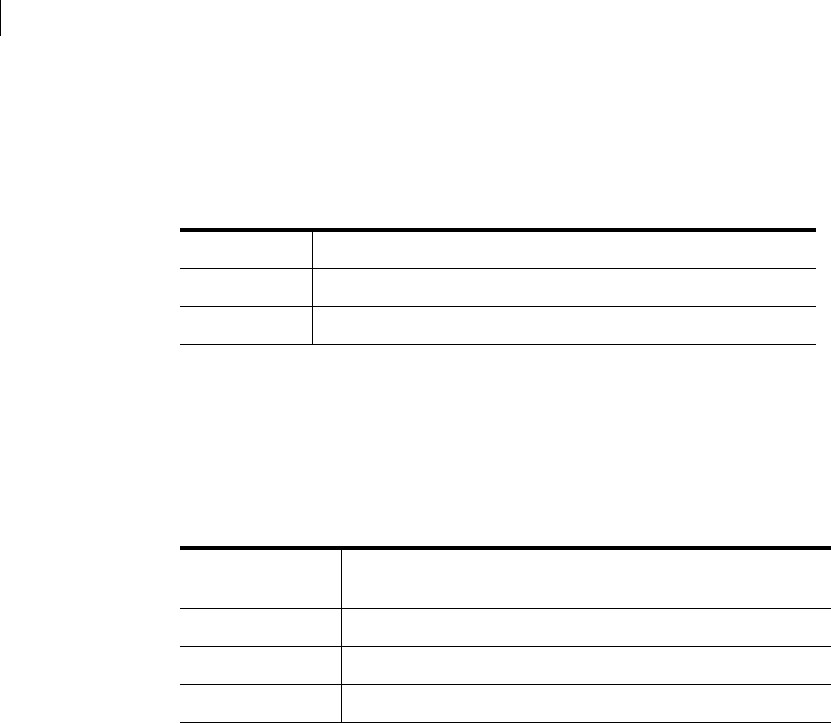
Table 9-1 Ghost Explorer arguments
-d1 Reports on corruptions or significant events in FAT file systems
-d2 Reports on corruptions or significant events in NTFS file systems
-d4 Reports on corruptions or significant events in Ext2/3 files
Table 9-2 Batch mode switches
-t Saves the list of directories in the dump file to a file with the same
name as the image file but with an extension of .txt
-tf Saves a list of directories and files
-tv Saves a verbose listing of directories and files
-t[vf]=filename Saves the list to the file specified


















