46 Understanding Veritas Volume Manager
Volume layouts in VxVM
Although both mirroring (RAID-1) and RAID-5 provide redundancy of data, they
use different methods. Mirroring provides data redundancy by maintaining
multiple complete copies of the data in a volume. Data being written to a
mirrored volume is reflected in all copies. If a portion of a mirrored volume fails,
the system continues to use the other copies of the data.
RAID-5 provides data redundancy by using parity. Parity is a calculated value
used to reconstruct data after a failure. While data is being written to a RAID-5
volume, parity is calculated by doing an exclusive OR (XOR) procedure on the
data. The resulting parity is then written to the volume. The data and calculated
parity are contained in a plex that is “striped” across multiple disks. If a portion
of a RAID-5 volume fails, the data that was on that portion of the failed volume
can be recreated from the remaining data and parity information. It is also
possible to mix concatenation and striping in the layout.
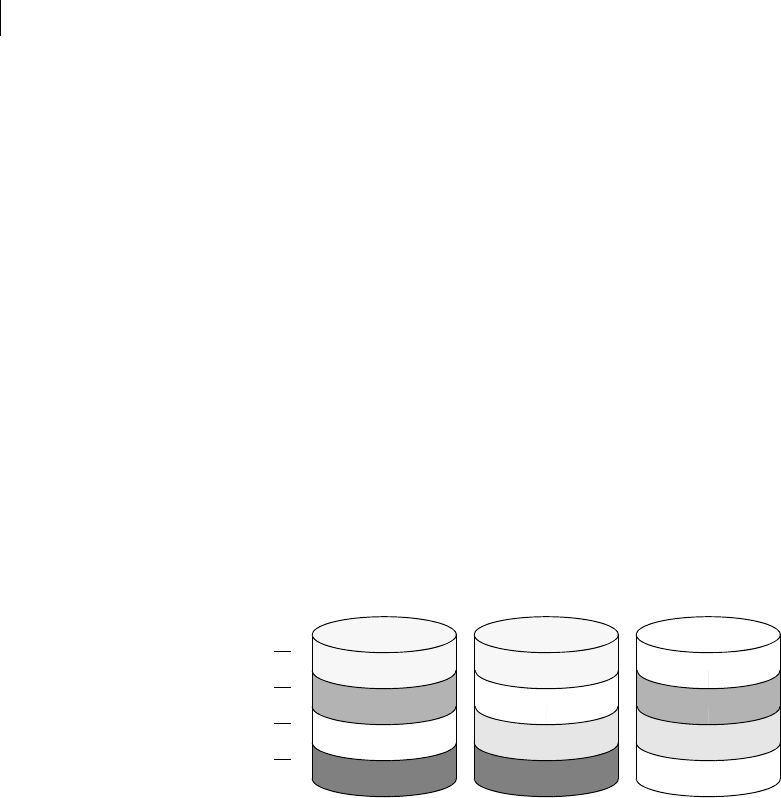
Figure 1-20 shows parity locations in a RAID-5 array configuration. Every stripe
has a column containing a parity stripe unit and columns containing data. The
parity is spread over all of the disks in the array, reducing the write time for
large independent writes because the writes do not have to wait until a single
parity disk can accept the data.
Figure 1-20 Parity locations in a RAID-5 mode
l
RAID-5 volumes can additionally perform logging to minimize recovery time.
RAID-5 volumes use RAID-5 logs to keep a copy of the data and parity currently
being written. RAID-5 logging is optional and can be created along with RAID-5
volumes or added later.
The implementation of RAID-5 in VxVM is described in “Veritas Volume
Manager RAID-5 arrays” on page 47.
Traditional RAID-5 arrays
A traditional RAID-5 array is several disks organized in rows and columns. A
column is a number of disks located in the same ordinal position in the array. A
row is the minimal number of disks necessary to support the full width of a
Parity
Parity
Data
Data
Data
Data
Data
Parity
Data
Data
Parity
Data
Stripe 1
Stripe 4
Stripe 3
Stripe 2