116 Chapter 5
Dual Arbitrary Waveform Generator
Using Waveform Clipping
How Clipping Reduces Peak-to-Average Power
You can reduce peak-to-average power, and consequently spectral regrowth, by clipping the waveform to a
selected percentage of its peak power. The PSG vector signal generator provides two different methods of
clipping: circular and rectangular.
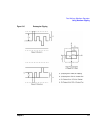
During circular clipping, clipping is applied to the combined I and Q waveform (|I + jQ|). Notice in Figure
5-15 that the clipping level is constant for all phases of the vector representation and appears as a circle.
During rectangular clipping, clipping is applied to the I and Q waveforms separately (|I|, |Q|). Notice in
Figure 5-16 on page 117 that the clipping level is different for I and Q; therefore, it appears as a rectangle in
the vector representation. With either method, the objective is to clip the waveform to a level that effectively
reduces spectral regrowth, but does not compromise the integrity of the signal. Figure 5-17 on page 118 uses
two complementary cumulative distribution plots to show the reduction in peak-to-average power that
occurs after applying circular clipping to a waveform.
The lower you set the clipping value, the lower the peak power that is passed (or the more the signal is
clipped). Often, the peaks can be clipped successfully without substantially interfering with the rest of the
waveform. Data that might be lost in the clipping process is salvaged because of the error correction inherent
in the coded systems. If you clip too much of the waveform, however, lost data is irrecoverable. You may
have to try several clipping settings to find a percentage that works well.
Figure 5-15 Circular Clipping