Section 5
ENGINE DC CONTROL SYSTEM
battery and starter should not exceed 0.12 VDC per
100 amperes of cranking current.
Select the battery cables based on total cable length
and prevailing ambient temperature. Generally, the
longer the cable and the colder the weather, the larg-
er the required cable diameter.
The following chart applies:
CABLE LENGTH (IN FEET) RECOMMENDED CABLE SIZE
0-10 No. 2
11-15 No. 0
16-20 No. 000
EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE:
Battery efficiency is greatly reduced by a decreased
electrolyte temperature. Such low temperatures have
a decided numbing effect on the electrochemical
action. Under high discharge rates (such as crank-
ing), battery voltage will drop to much lower values in
cold temperatures than in warmer temperatures. The
freezing point of battery electrolyte fluid is affected by
the state of charge of the electrolyte as indicated
below:
SPECIFIC GRAVITY FREEZING POINT
1.220 -35° F. (-37° C.)
1.200 --20° F. (-29° C.)
1.160 0° F. (-18° C.)
ADDING WATER:
Water is lost from a battery as a result of charging
and discharging and must be replaced. If the water is
not replaced and the plates become exposed, they
may become permanently sulfated. In addition, the
plates cannot take full part in the battery action unless
they are completely immersed in electrolyte. Add only
DISTILLED WATER to the battery. DO NOT USE
TAP WATER.
NOTE: Water cannot be added to some “mainte-
nance-free” batteries.
CHECKING BATTERY STATE OF CHARGE:
Use an automotive type battery hydrometer to test the
battery state of charge. Follow the hydrometer manu-
facturer's instructions carefully. Generally, a battery
may be considered fully charged when the specific
gravity of its electrolyte is 1.260. If the hydrometer
used does not have a “Percentage of Charge” scale,
compare the readings obtained with the following:
SPECIFIC GRAVITY PERCENTAGE OF CHARGE
1.260 100%
1.230 75%
1.200 50%
1.170 25%
CHARGING A BATTERY:
Use an automotive type battery charger to recharge a
battery. Battery fluid is an extremely corrosive, sulfu-
ric acid solution that can cause severe burns. For that
reason, the following precautions must be observed:
• The area in which the battery is being charged must
be well ventilated. When charging a battery, an
explosive gas mixture forms in each cell.
• Do not smoke or break a live circuit near the top of
the battery. Sparking could cause an explosion.
• Avoid spillage of battery fluid. If spillage occurs,
flush the affected area with clear water immediately.
• Wear eye protection when handling a battery.
Page 25
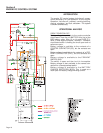
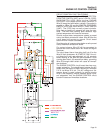
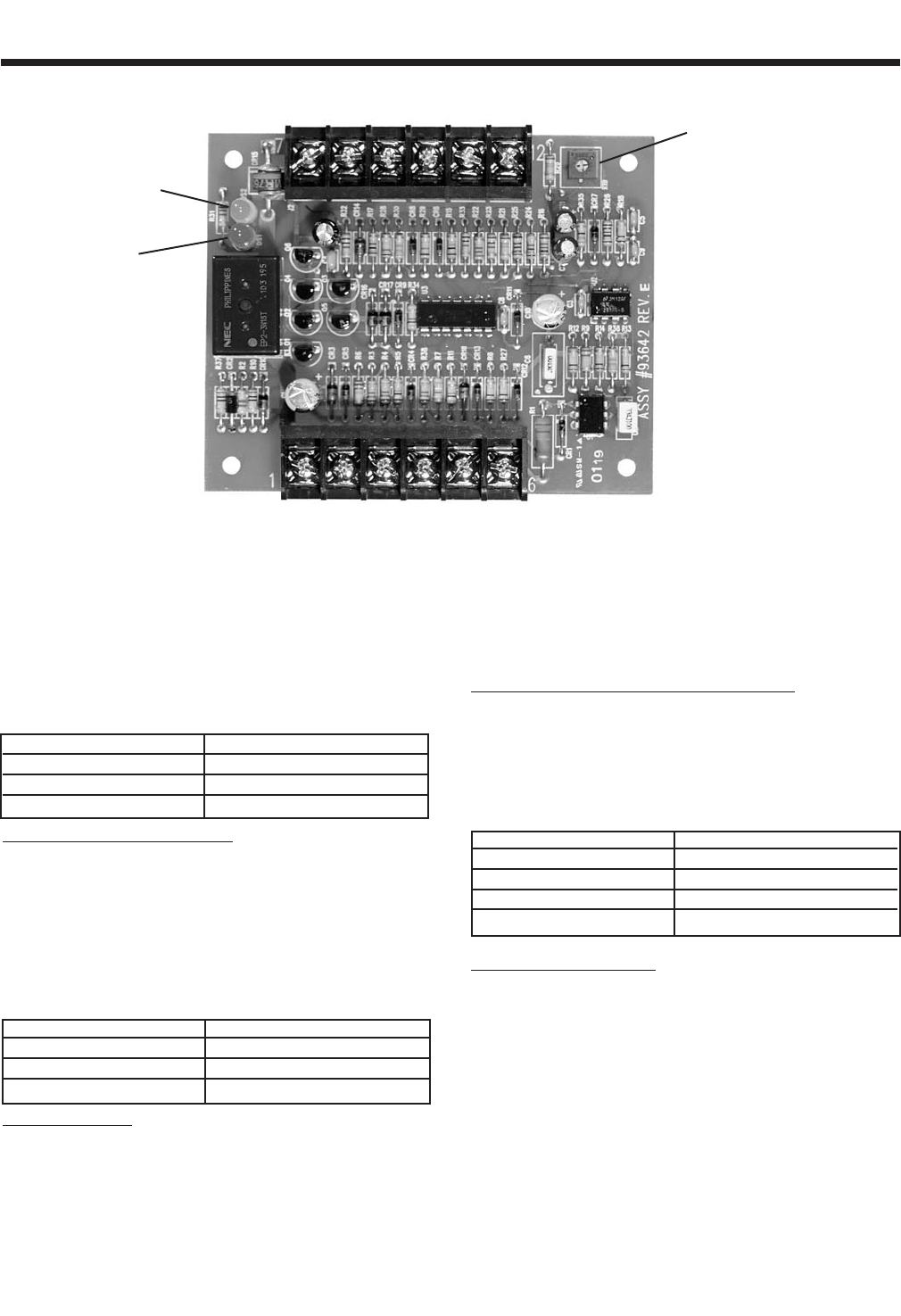
GREEN LED
TERMINALS:
OVERSPEED
SHUTDOWN
POTENTIOMETER
1 2 3 4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12
TERMINALS:
RED LED
Figure 5-4 – Engine Control Circuit Board