14-1
14. Setting Up SSL Encryption
This section describes the procedure for setting up a secure connection via an https
web connection to the MPC.
Note: SSL parameters cannot be defined via the Web Browser Interface. In
order to set up SSL encryption, you must contact the MPC via the Text Interface.
There are two different types of https security certificates: "Self Signed" certificates and
"Signed" certificates.
Self Signed certificates can be created by the MPC, without the need to go to an outside
service, and there is no need to set up your domain name server to recognize the MPC.
The principal disadvantage of Self Signed certificates, is that when you access the MPC
command mode via the Web Browser Interface, the browser will display a message
which warns that the connection might be unsafe. Note however, that even though this
message is displayed, communication will still be encrypted, and the message is merely
a warning that the MPC is not recognized and that you may not be connecting to the
site that you intended.
Signed certificates must be created via an outside security service (e.g., VeriSign
®
,
Thawte™, etc.) and then uploaded to the MPC unit to verify the user's identity. In order
to use Signed certificates, you must contact an appropriate security service and set up
your domain name server to recognize the name that you will assign to the MPC unit
(e.g., service.wti.com.) Once a signed certificate has been created and uploaded to
the MPC, you will then be able to access command mode without seeing the warning
message that is normally displayed for Self Signed certificate access.
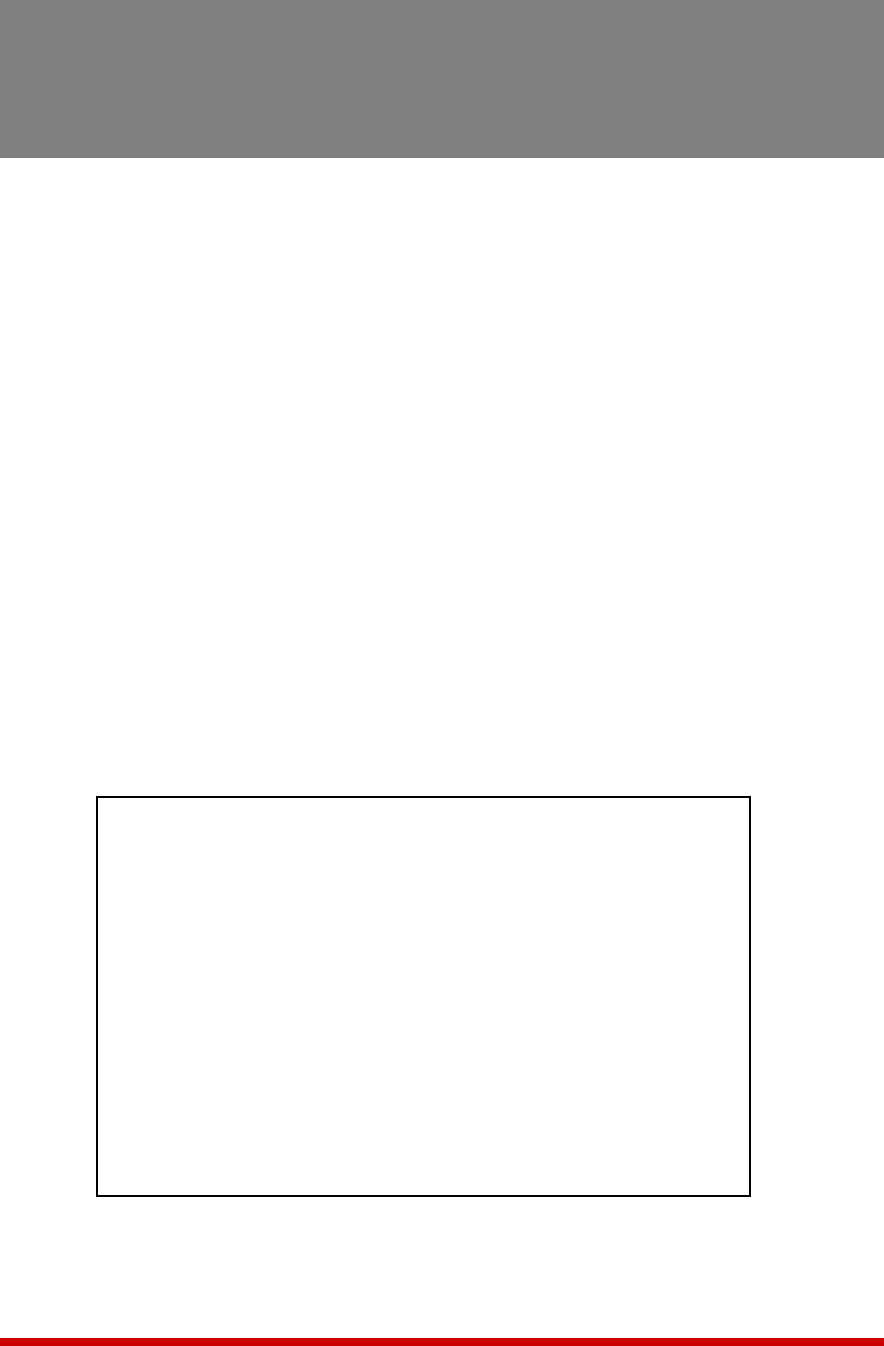
WEB ACCESS:
HTTP:
1. Enable: On
2. Port: 80
HTTPS:
3. Enable: On
4. Port: 443
SSL Certificates:
5. Common Name:
6. State or Province:
7. Locality:
8. Country:
9. Email Address:
10. Organization Name:
11. Organizational Unit:
12. Create CSR:
13. View CSR:
14. Import CRT:
Enter: #<CR> to change,
<ESC> to return to previous menu ...
Figure 14.1: Web Access Parameters (Text Interface Only)


















