6-34 489 Generator Management Relay GE Multilin
6.3 MODBUS MEMORY MAP 6 COMMUNICATIONS
6
6.3.8 MEMORY MAP DATA FORMATS
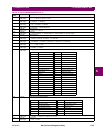
Table 6–2: DATA FORMATS (SHEET 1 OF 5)
FORMAT
CODE
TYPE DEFINITION
F1 16 bits Unsigned Value
Example: 1234 stored as 1234
F2 16 bits Unsigned Value, 1 Decimal Place
Example: 123.4 stored as 1234
F3 16 bits Unsigned Value, 2 Decimal Places
Example: 12.34 stored as 1234
F4 16 bits 2’s Complement Signed Value
Example, –1234 stored as –1234 (i.e., 64302)
F5 16 bits 2’s Complement Signed Value, 1 Decimal Place
Example, –1.234 stored as –1234 (i.e., 64302)
F6 16 bits 2’s Complement Signed Value, 2 Decimal Places
Example, –12.34 stored as –1234 (i.e., 64302)
F10 32 bits 2’s Complement Signed Long Value, 1 Decimal Place
1st 16 bits: High order word of long value
2nd 16 bits: Low order word of long value
Example: –12345.6 stored as –123456 (i.e., 1st word FFFE hex, 2nd word 1DC0 hex)
F12 32 bits 2’s Complement Signed Long Value
1st 16 bits: High order word of long value
2nd 16 bits: Low order word of long value
Example: –123456 stored as 1st word FFFE hex, 2nd word 1DC0 hex
F13 32 bits 2’s Compliment Signed Long Value, 3 Decimal Places
1st 16 bits: High order word of long value
2nd 16 bits: Low order word of long value
Example: –123.456 stored as -123456 (i.e., 1st word FFFE hex, 2nd word 1DC0 hex)
F14 32 bits 2’s Complement Signed Long Value, 2 Decimal Places
1st 16 bits: High order word of long value
2nd 16 bits: Low order word of long value
Example: –1234.56 stored as –123456 (i.e., 1st word FFFE hex, 2nd word 1DC0 hex)
F15 16 bits Hardware Revision
1 = revision A, 2 = revision B, 3 = revision C,..., 26 = revision Z
F16 16 bits Software Revision
1111 1111 XXXX XXXX: Major revision number – 0 to 9 in steps of 1
XXXX XXXX 1111 1111: Minor revision number (two BCD digits) 00 to 99 in steps of 1
Example: Revision 2.30 stored as 0230 hex
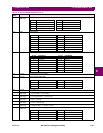
F18 32 bits Date (MM/DD/YYYY)
1st byte: Month (1 to 12)
2nd byte: Day (1 to 31)
3rd and 4th byte: Year (1996 to 2094)
Example: Feb. 20, 1996 stored as 34867148 (i.e., first word 0214, 2nd word 07CC)
F19 32 bits Time (HH:MM:SS:hh)
1st byte: Hours (0 to 23)
2nd byte: Minutes (0 to 59)
3rd byte: Seconds (0 to 59)
4th byte: Hundredths of seconds (0 to 99)
Example: 2:05pm stored as 235208704 (i.e., 1st word 0E05, 2nd word 0000)
F22 16 bits Character String (Note: Range indicates number of characters)
1st byte (MSB) of each word: First of a pair of characters
2nd byte (LSB) of each word: Second of a pair of characters
Example: String “AB” stored as 4142 hex
F24 32 bits Time Format for Broadcast
1st byte: Hours (0 to 23)
2nd byte: Minutes (0 to 59)
3rd and 4th bytes: Milliseconds (0 to 59999). Note: Clock resolution limited to 1/100 sec.
Example: 1:15:48:572 stored as 17808828 (i.e., 1st word 010F, 2nd word BDBC)
F50 16 bits Relay List (Bitmap)
Bit 0 = Relay 1, Bit 1 =Relay 2, Bit 2 = Relay 3, Bit 3 = Relay 4, Bit 4 = Relay 5, Bit 5 = Relay 6
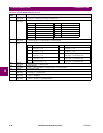
F100 Unsigned
16 bit integer
Temperature display units
0 = Celsius, 1 = Fahrenheit
F101 Unsigned
16 bit integer
RS485 baud rate
0 = 300, 1 = 1200, 2 = 2400, 3 = 4800, 4 = 9600, 5 = 19200
F102 Unsigned
16 bit integer
RS485 parity
0 = None, 1 = Odd, 2 = Even
F103 Unsigned
16 bit integer
No / Yes selection
0 = No, 1 = Yes
F104 Unsigned
16 bit integer
Ground CT type
0 = None, 1 = 1 A Secondary, 2 = 50:0.025 Ground CT, 3 = 5 A Secondary
F105 Unsigned
16 bit integer
Off / On selection
0 = Off, 1 = On
F106 Unsigned
16 bit integer
VT connection type
0 = None, 1 = Open Delta, 2 = Wye