GE Multilin 489 Generator Management Relay 4-67
4 SETPOINTS 4.10 S9 THERMAL MODEL
4
f) HOT/COLD CURVE RATIO
When thermal limit information is available for both a hot and cold machine, the 489 thermal model will adapt for the condi-
tions if the HOT/COLD CURVE RATIO is programmed. The value entered for this setpoint dictates the level of thermal capacity
used that the relay will settle at for levels of current that are below the OVERLOAD PICKUP LEVEL. When the generator is run-
ning at a level below the OVERLOAD PICKUP LEVEL, the thermal capacity used will rise or fall to a value based on the aver-
age phase current and the entered
HOT/COLD CURVE RATIO. Thermal capacity used will either rise at a fixed rate of 5% per
minute or fall as dictated by the running cool time constant.
(EQ 4.33)
where: TC
used_end
= Thermal Capacity Used if I
per_unit
remains steady state
I
eq
= equivalent generator heating current
hot/cold = HOT/COLD CURVE RATIO setpoint
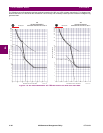
The hot/cold curve ratio may be determined from the thermal limit curves, if provided, or the hot and cold safe stall times.
Simply divide the hot safe stall time by the cold safe stall time. If hot and cold times are not provided, there can be no differ-
entiation and the HOT/COLD CURVE RATIO should be entered as "1.00".
g) RTD BIAS
The thermal replica created by the features described in the sections above operates as a complete and independent
model. However, the thermal overload curves are based solely on measured current, assuming a normal 40°C ambient and
normal machine cooling. If there is an unusually high ambient temperature, or if machine cooling is blocked, generator tem-
perature will increase. If the stator has embedded RTDs, the 489 RTD bias feature should be used to correct the thermal
model.
The RTD bias feature is a two part curve, constructed using 3 points. If the maximum stator RTD temperature is below the
RTD BIAS MINIMUM setpoint (typically 40°C), no biasing occurs. If the maximum stator RTD temperature is above the RTD
BIAS MAXIMUM setpoint (typically at the stator insulation rating or slightly higher), then the thermal memory is fully biased
and thermal capacity is forced to 100% used. At values in between, the present thermal capacity used created by the over-
load curve and other elements of the thermal model, is compared to the RTD Bias thermal capacity used from the RTD Bias
curve. If the RTD Bias thermal capacity used value is higher, then that value is used from that point onward. The
RTD BIAS
CENTER POINT should be set at the rated running temperature of the machine. The 489 automatically determines the ther-
mal capacity used value for the center point using the HOT/COLD SAFE STALL RATIO setpoint.
(EQ 4.34)
At temperatures less that the RTD_Bias_Center temperature,
(EQ 4.35)
At temperatures greater than the RTD_Bias_Center temperature,
(EQ 4.36)
where: RTD_Bias_TCused = TC used due to hottest stator RTD
Temp
acutal
= current temperature of the hottest stator RTD
Temp
min
= RTD Bias minimum setpoint
Temp
center
= RTD Bias center setpoint
Temp
max
= RTD Bias maximum setpoint
TCused @ RTD_Bias_Center = TC used defined by the
HOT/COLD SAFE STALL RATIO setpoint
In simple terms, the RTD bias feature is real feedback of measured stator temperature. This feedback acts as correction of
the thermal model for unforeseen situations. Since RTDs are relatively slow to respond, RTD biasing is good for correction
and slow generator heating. The rest of the thermal model is required during high phase current conditions when machine
heating is relatively fast.
TC
used_end
I
eq
1
hot
cold
---------- -–
⎝⎠
⎛⎞
100%××=
TC
used
@ RTD_Bias_Center 1
hot
cold
---------- -–
⎝⎠
⎛⎞
100%×=
RTD_Bias_TC
used
Temp
actual
Temp
min
–
Temp
center
Temp
min
–
--------------------------------------------------------
100 TC
used
@ RTD_Bias_Center–()× TC
used
@ RTD_Bias_Center+=
RTD_Bias_TC
used
Temp
actual
Temp
center
–
Temp
max
Temp
center
–
-------------------------------------------------------------
100 TC
used
@ RTD_Bias_Center–()× TC
used
@ RTD_Bias_Center+=