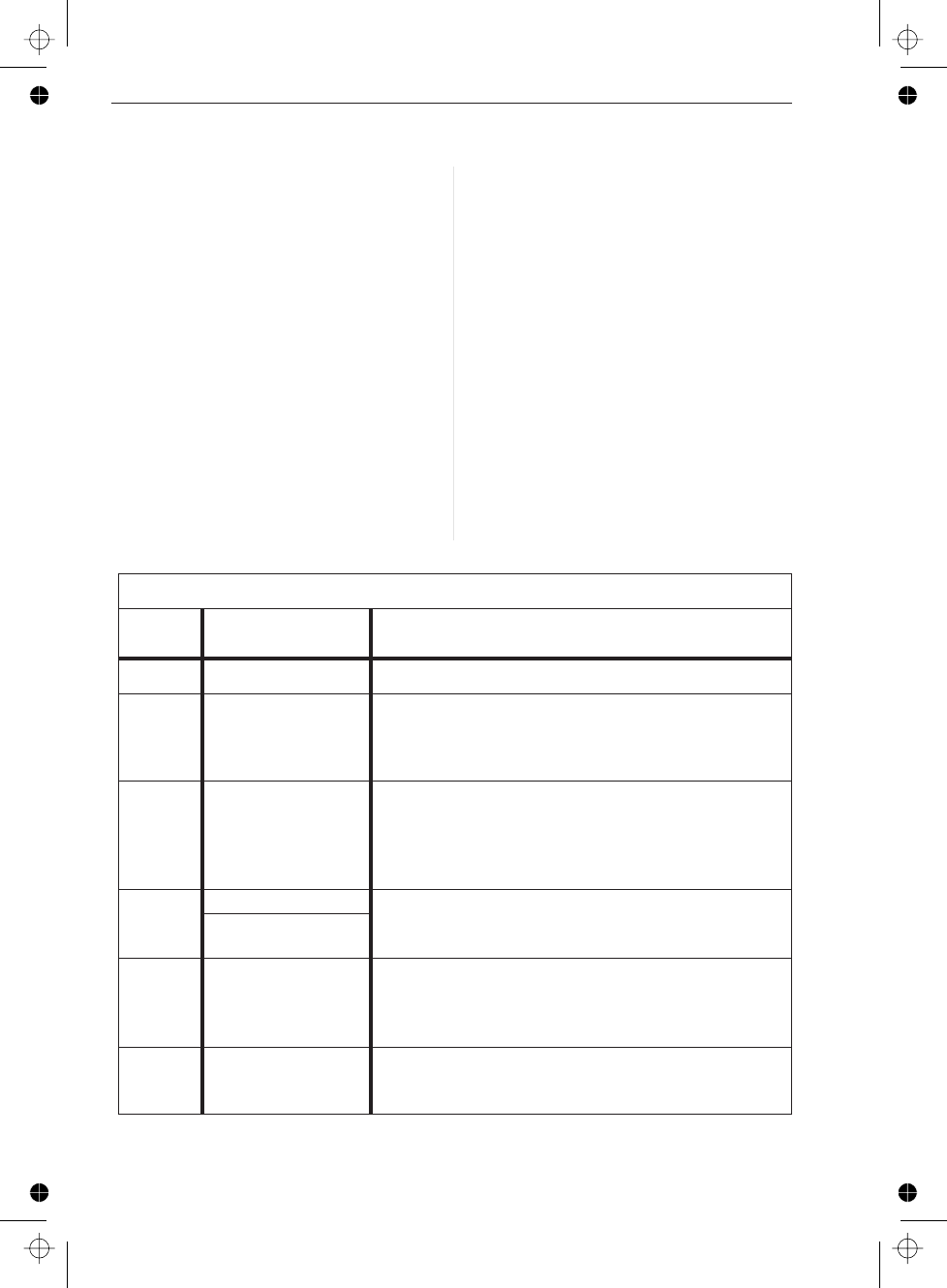
Command Errors
Error
Number
Error Description Description/Explanation/Examples
0
No error
–100
Command error This is the generic syntax error for devices that can-
not detect more specific errors. This code indicates
only that a Command Error defined in IEEE-488.2,
11.5.1.1.4 has occurred.
–101
Invalid character A syntactic element contains a character which is in
-
valid for that type; for example, a header containing
an ampersand, SETUP&. This error might be used
in place of errors –114, –121, –141, and perhaps
some others.
–102
Syntax error An unrecognized command or data type was encoun
-
tered; for example, a string was received when the
counter does not accept strings.
Syntax error; unrec
-
ognized data
–103
Invalid separator The parser was expecting a separator and encoun
-
tered an illegal character; for example, the semico
-
lon was omitted after a program message unit,
∗EMC1:CH1:VOLTS5.
–104
Data type error The parser recognized a data element different than
one allowed; for example, numeric or string data
was expected but block data was encountered.
Error Messages
8-2 Error Code 0 to -104
Read the Error/Event Queue
You read the error queue with the :SYS
-
Tem:ERRor? query.
Example:
SEND→
:SYSTem:ERRor?
READ←
–100, “Command Error”
The query returns the error number fol
-
lowed by the error description.
If more than one error occurred, the query
will return the error that occurred first.
When you read an error, you will also re
-
move it from the queue. You can read the
next error by repeating the query. When
you have read all errors, the queue is
empty, and the :SYSTem:ERRor?
query will return:
0, “No error”
When errors occur and you do not read
these errors, the Error Queue may over
-
flow. Then the instrument will overwrite
the last error in the queue with:
–350, “Queue overflow”
If more errors occur they will be dis
-
carded.
+
Read more about how to use er
-
ror reporting in the Introduction to
SCPI chapter


















