SECTION 2.1
DESCRIPTION & COMPONENTS
AC GENERATORS
PART 2
Page 2.1-2
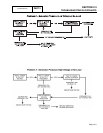
Figure 2. The 2-Pole Rotor Assembly
STATOR
ASSEMBLY
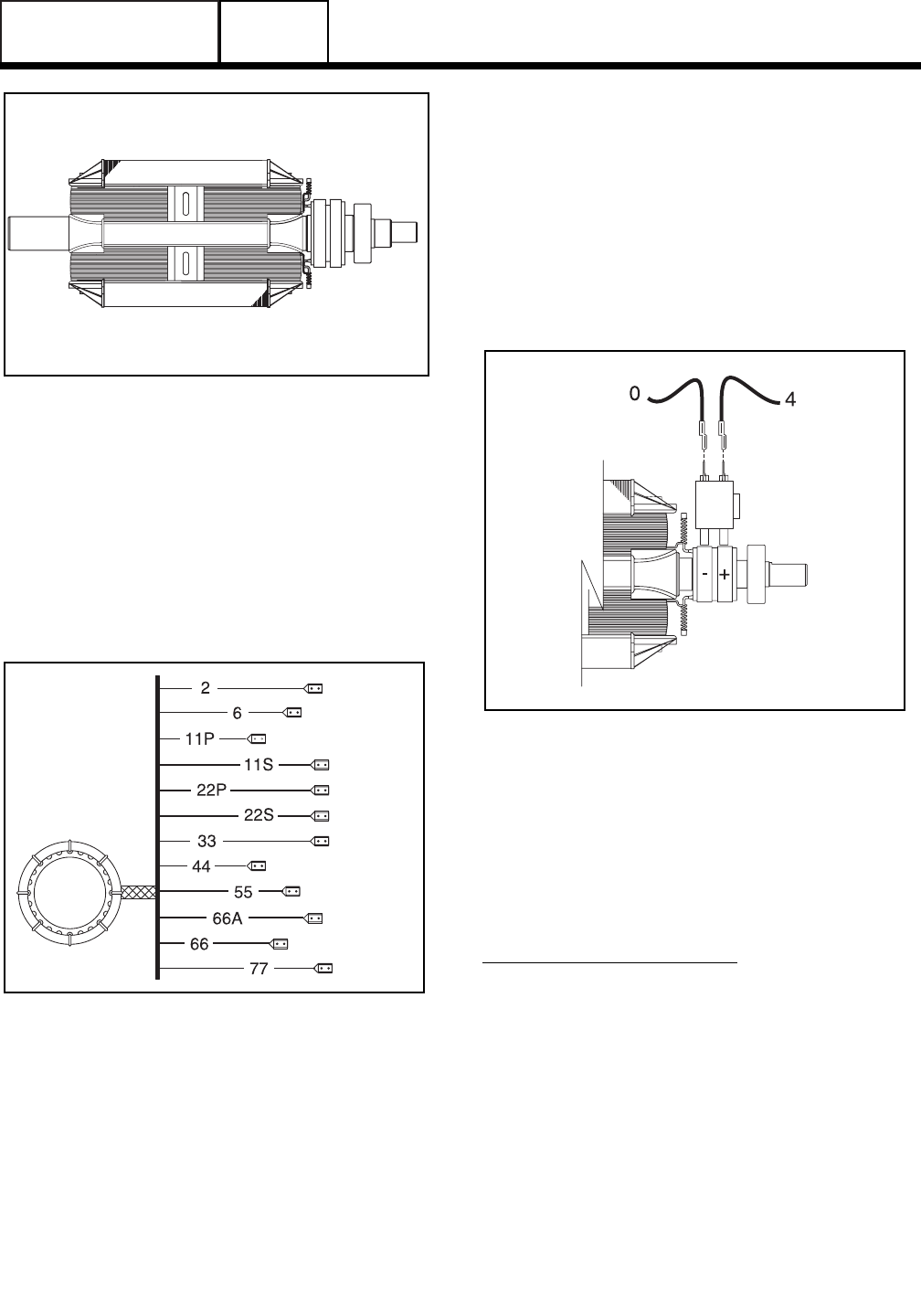
The stator can houses and retains (a) dual AC power
windings, (b) excitation winding, (c) battery charge
winding and (d) engine run winding. A total of twelve
(12) stator leads are brought out of the stator can as
shown in Figure 3.
The stator can is sandwiched between an engine
adapter and a rear bearing carrier. It is retained in
that position by four stator studs.
Figure 3 Stator Assembly Leads
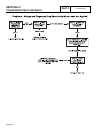
BRUSH
HOLDER
AND
BRUSHES
The brush holder is retained to the rear bearing carrier
by means of two #10-32 x 9/16 Taptite screws. A
positive (+) and a negative (-) brush are retained in the
brush holder, with the positive (+) brush riding on the
slip ring nearest the rotor bearing.
Wire 4 connects to the positive (+) brush and Wire 0 to
the negative (-) brush. Wire 0 connects to frame
ground. Rectified and regulated excitation current, as
well as current from a field boost circuit, are delivered
to the rotor windings via Wire 4, and the positive (+)
brush and slip ring. The excitation and field boost
current passes through the windings and to frame
ground via the negative (-) slip ring and brush, and
Wire 0. This current flow creates a magnetic field
around the rotor having a flux concentration that is
proportional to the amount of current flow.
Figure 4. Brush Holder and Brushes
OTHER AC GENERATOR COMPONENTS
Some AC generator components are housed in the
generator control panel enclosure, and are not shown
in Figure 1. These are (a) an excitation circuit breaker,
(b) a voltage regulator, and (c) a main line circuit
breaker.
EXCITATION CIRCUIT BREAKER:
The excitation circuit breaker (CB2) is housed in the
generator panel enclosure and electrically connected
in series with the excitation (DPE) winding output to
the voltage regulator. The breaker is self-resetting, i.e.;
its contacts will close again when excitation current
drops to a safe value.
If the circuit breaker has failed open, excitation current
flow to the voltage regulator and, subsequently, to the
rotor windings will be lost. Without excitation current
flow, AC voltage induced into the stator AC power
windings will drop to a value that is commensurate with
the rotor residual magnetism (see Figure 5).