Section 3
Receiving & Installation
Receiving & Installation 3‐1MN2408
Receiving & Inspection When you receive your generator, there are several things you should do immediately.
1. Observe the condition of the shipping container and report any damage immediately to
the commercial carrier that delivered your system.
2. Verify that the part number of the system you received is the same as the part number
listed on your purchase order.
3. If the system is to be stored for several weeks before use, be sure that it is stored in a
location that conforms to published storage temperature and humidity specifications.
Lifting the Generator When lift or hoist equipment is used to lift the generator and move it to position, be careful not
to contact overhead wires or other obstacles. Be sure lift or hoist equipment has appropriate tires
for the terrain to avoid becoming stuck or tipping over. If the shipping pallet is intact, use a fork lift
to move the generator. If the shipping pallet has been removed, use two steel pipes through the “Lift
Point” holes to lift the generator. See Figure 3‐1.
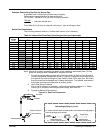
Figure 3‐1 Generator Lifting
Lift Point
Lift
Point
Height
Width
Length
To lift the generator, always use spreader bars,
chains, eyehooks and other hardware that is of
sufficient strength to lift at least three times the
weight of the generator.
Physical Location The mounting location of the system is important. It should be installed in an area that is
protected from direct harmful gases or liquids, dust, metallic particles, shock and vibration.
It should be installed in an outdoor location so the exhaust fumes are vented to the atmosphere.
When the Generator is installed outdoors
The factory installed enclosure is designed to keep out undesirable weather elements while
providing cooling and ventilation.
When the Generator is installed in a building it is essential to provide:
1. Adequate control and exhausting of the heated air.
2. An adequate and constant supply of incoming cooling air.
3. Adequate control and discharge of the engine's hot exhaust gases.
4. Adequate ventilation of the building when the engine shuts down.