SSeeccttiioonn 11
GGEENNEERRAATTOORR FFUUNNDDAAMMEENNTTAALLSS
NOTE: AC output frequency at 3720 rpm will be
about 62 Hertz. The “No-Load” is set slightly high
to prevent excessive rpm, frequency and voltage
droop under heavy electrical loading.
Generator operation may be described briefly as fol-
lows:
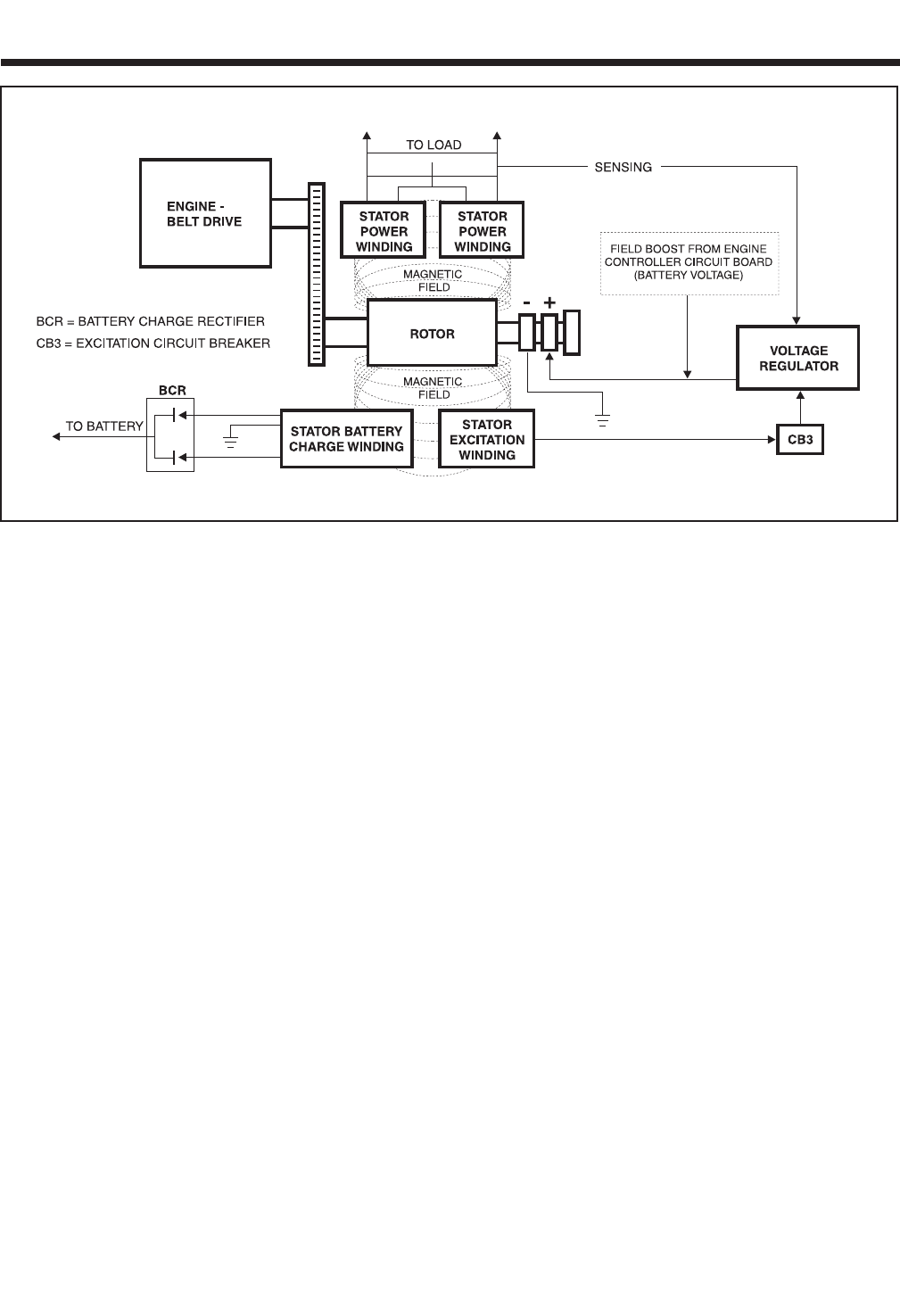
1. Some “residual” magnetism is normally present in the Rotor
and is sufficient to induce approximately 7 to 12 volts AC Into
the STATOR's AC power windings.
2. During startup, an engine controller circuit board delivers bat-
tery voltage to the ROTOR, via the brushes and slip rings.
a. The battery voltage is called “Field Boost”.
b. Flow of direct current through the ROTOR
increases the strength of the magnetic field
above that of “residual” magnetism alone.
3. “Residual” plus “Field Boost” magnetism induces a voltage into
the Stator excitation (DPE), battery charge and AC Power
windings.
4. Excitation winding unregulated AC output is delivered to an
electronic voltage regulator, via an excitation circuit breaker.
a. A “Reference” voltage has been preset into
the Voltage Regulator.
b. An “Actual” (“sensing”) voltage is delivered
to the Voltage Regulator via sensing leads
from the Stator AC power windings.
c. The Regulator “compares” the actual (sens-
ing) voltage to its pre-set reference voltage.
(1) If the actual (sensing) voltage is greater
than the pre-set reference voltage, the
Regulator will decrease the regulated cur-
rent flow to the Rotor.
(2) If the actual (sensing) voltage is less
than the pre-set reference voltage, the
Regulator will increase the regulated cur-
rent flow to the Rotor.
(3) In the manner described, the Regulator
maintains an actual (sensing) voltage that is
equal to the pre-set reference voltage.
NOTE: The Voltage Regulator also changes the
Stator excitation windings alternating current
(AC) output to direct current (DC).
5. When an electrical load is connected across the Stator power
windings, the circuit is completed and an electrical current will
flow.
6. The Rotor's magnetic field also induces a voltage Into the
Stator battery charge windings.
a. Battery charge winding AC output is deliv-
ered to a battery charge rectifier (BCR)
which changes the AC to direct current
(DC).
b. The rectified DC is then delivered to the unit
battery, to maintain the battery in a charged
state.
c. A 1 ohm, 25 watt Resistor is installed in
series with the grounded side of the battery
charge circuit.
Page 5
Figure 1-7. – Generator Operating Diagram