SSeeccttiioonn 77
DDIIAAGGNNOOSSTTIICC TTEESSTTSS
RESULTS:
1. If
“
Continuity” is not measured in Step 1, repair or replace Wire
0 between the Starter Contactor Relay and the ground terminal.
2. If
“
Continuity” was not measured in Step 2 when the Start-Stop
switch was activated to “START”, replace the Starter Contactor
Relay.
3. If
“
Continuity” is measured in Step 2, go to Test 26A.
TEST 26A - CHECK STARTER CONTACTOR
DISCUSSION:
The Starter Contactor (SC) must energize and it's
heavy duty contacts must close or the engine will not
crank. This test will determine if the Starter Contactor
is in working order. The Starter Contactor is connect-
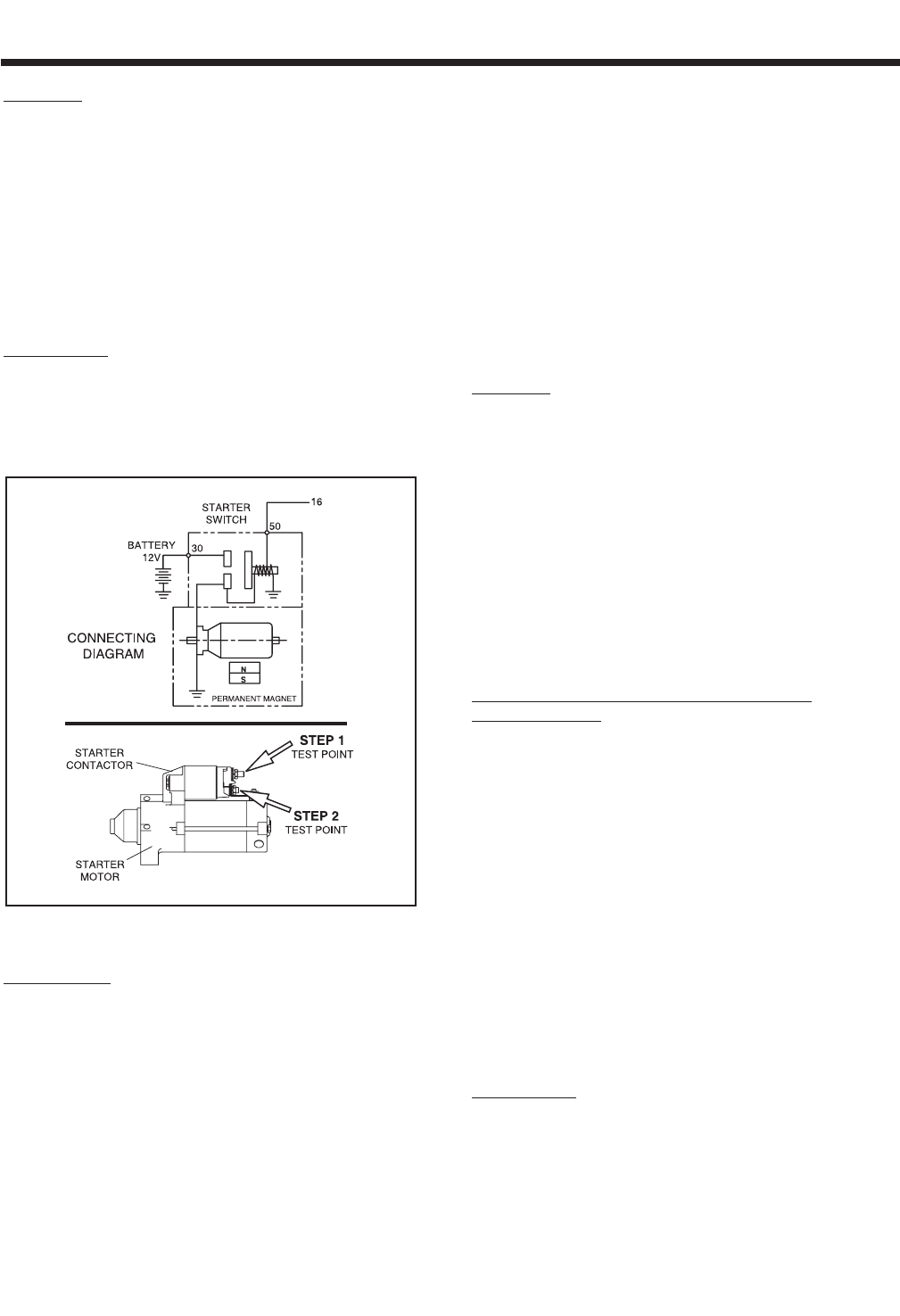
ed to the Starter Motor (see Figure 7-20).
Figure 7-20. – The Starter Contactor (SC)
PROCEDURE:
1. Carefully inspect the starter motor cable that runs from the
Battery to the Starter Motor. Cable connections should be
clean and tight. If connections are dirty or corroded, remove
cable and clean cable terminals and studs. Replace any cable
that is defective or badly corroded. Set the VOM to measure
DC voltage. Connect the positive (+) meter test lead to the
Starter Contactor stud that the battery cable is connected to.
Connect the negative (-) meter test lead to a clean frame
ground. Battery voltage should be measured (see Figure 7-20,
STEP 1 TEST POINT).
2. Set the VOM to measure DC voltage. Disconnect Wire 16 from
the Starter Contactor. Connect the positive (+) meter test lead
to Wire 16. Connect the negative (-) meter test lead to a clean
frame ground. Set the Start-Stop Switch to “START”. Battery
voltage should be indicated. Reconnect Wire 16 to the Starter
Contactor.
3. Set the VOM to measure DC voltage. Connect the positive (+)
meter test lead to the Starter Contactor stud that has the small
jumper wire connected to the Starter. Connect the negative (-)
meter test lead to a clean frame ground. Set the Start-Stop
Switch to “START”. Battery voltage should be measured (see
Figure 7-20, STEP 2 TEST POINT).
RESULTS:
1. If battery voltage was not measured in Step 1, repeat Test 22.
2. If battery voltage was not measured in Step 2, repair or
replace Wire 16 between the Starter Contactor Relay (SCR)
and the Starter Contactor (SC).
3 If battery voltage was measured in Step 1, but not in Step 3,
replace the Starter Contactor.
4. If battery voltage was measured in Step 3 but the engine still
does not crank, go to test 27.
TEST 27 - CHECK STARTER MOTOR
CONDITIONS AFFECTING STARTER MOTOR
PERFORMANCE:
1. A binding or seizing condition in the Starter Motor bearings.
2. A shorted, open or grounded armature.
a.Shorted, armature (wire insulation worn and
wires touching one another). Will be indicated
by low or no RPM.
b.Open armature (wire broken) will be indicated
by low or no RPM and excessive current draw.
c.Grounded armature (wire insulation worn and
wire touching armature lamination or shaft). Will
be indicated by excessive current draw or no
RPM.
3. A defective Starter Motor switch.
4. Broken, damaged or weak magnets.
5. Starter drive dirty or binding.
DISCUSSION:
Test 25 verified that circuit board action is delivering
DC voltage to the Starter Contactor Relay (SCR).
Test 26 verified the operation of the SCR. Test 26A
verified the operation of the Starter Contactor (SC).
Another possible cause of an "engine won't crank"
problem is a failure of the Starter Motor.
Page 52


















