SSeeccttiioonn 77
DDIIAAGGNNOOSSTTIICC TTEESSTTSS
INTRODUCTION
The “Diagnostic Tests” in this chapter may be per-
formed in conjunction with the “Flow Charts” of
Section 6. Test numbers in this chapter correspond to
the numbered tests in the “Flow Charts”.
Tests 1 through 17 are procedures Involving prob-
lems with the generator's AC output voltage and fre-
quency (Problems 1 through 4 in the “Flow Charts”).
Tests 18 through 42 are procedures involving prob-
lems with engine operation (Problems 5 through 9 in
the “Troubleshooting Flow Charts”).
You may wish to read Section 4, “Measuring
Electricity”.
NOTE: Test procedures in this Manual are not
necessarily the only acceptable methods for diag-
nosing the condition of components and circuits.
All possible methods that might be used for sys-
tem diagnosis have not been evaluated. If you use
any diagnostic method other than the method
presented in this Manual, you must ensure that
neither your safety nor the product's safety will
be endangered by the procedure or method you
have selected.
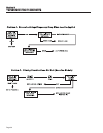
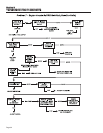
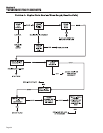
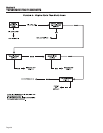
TEST 1- CHECK NO-LOAD VOLTAGE AND
FREQUENCY
DISCUSSION:
The first step in analyzing any problem with the AC
generator is to determine the unit's AC output voltage
and frequency. Once that has been done, you will
know how to proceed with specific diagnostic tests.
PROCEDURE:
1. Set a volt-ohm-milliammeter (VOM) to read AC voltage.
Connect the meter test leads across customer connection
leads T1 (Red) and T2 (White).
2. Disconnect or turn OFF all electrical loads. Initial checks and
adjustments are accomplished at no-load.
3. Start the engine, let it stabilize and warm up.
4. Read the AC voltage.
5. Connect an AC frequency meter across AC output leads T1
(Red) and T2 (White). Repeat the above procedure.
RESULTS:
For units rated 60 Hertz, no-load voltage and frequen-
cy should be approximately 122-126 VAC and 61-63
Hertz respectively.
1. If AC voltage and frequency are BOTH correspondingly high or
low, go to Test 2.
2. If AC frequency is good but low or residual voltage is indicated,
go to Test 3.
3. If AC output voltage and frequency are both “zero”, go to Test 12.
4. If the no-load voltage and frequency are within the stated limits,
go to Test 13.
NOTE: The term “low voltage” refers to any volt-
age reading that is lower than the unit's rated
voltage. The term “residual voltage” refers to the
output voltage supplied as a result of Rotor resid-
ual magnetism (approximately 5-12 VAC).
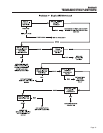
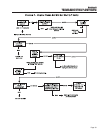
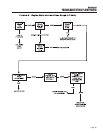
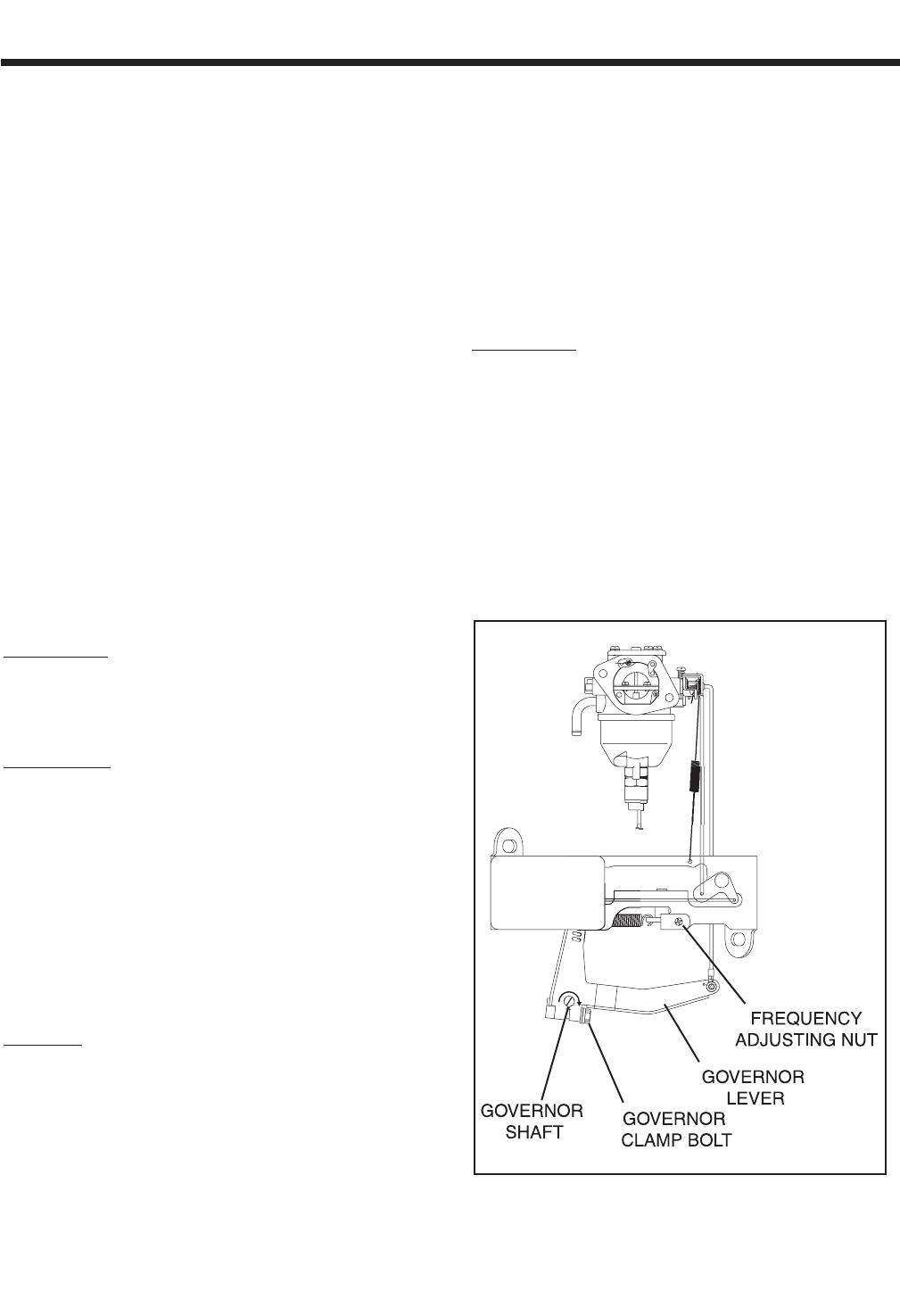
TEST 2- CHECK ENGINE GOVERNOR
DISCUSSION:
Rotor operating speed and AC output frequency are
proportional. The generator will deliver a frequency of
60 Hertz at 3600 Rotor rpm or 62 Hertz at 3720
Rotor rpm.
The Voltage Regulator should be adjusted to deliver
120 VAC (line-to-neutral) at a frequency of 60 Hertz
or 124 VAC (line-to-neutral at 62 Hertz. It is apparent
that, if governed speed is high or low, AC frequency
and voltage will be correspondingly high or low.
Governed speed at no-load is usually set slightly
above the rated speed of 60 Hertz (to 62 Hertz), to
prevent excessive rpm, frequency and voltage droop
under heavy electrical loading.
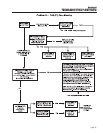
Figure 7-1. – Governor Adjustment Points
Page 38