SECTION 6 GPIB
6-7
6.2.6 Parameter
The table below shows the parameter types employed for this instrument.
In this manual, these parameter types are written in lower-case alphabetical characters between brackets < >, and
the IEEE488.2 (or SCPI)-defined <PROGRAM TYPE>s corresponding to them are written in upper-case alphabetical
characters. The correspondence between each parameter and IEEE488.2 (or SCPI) is written for the various
commands.
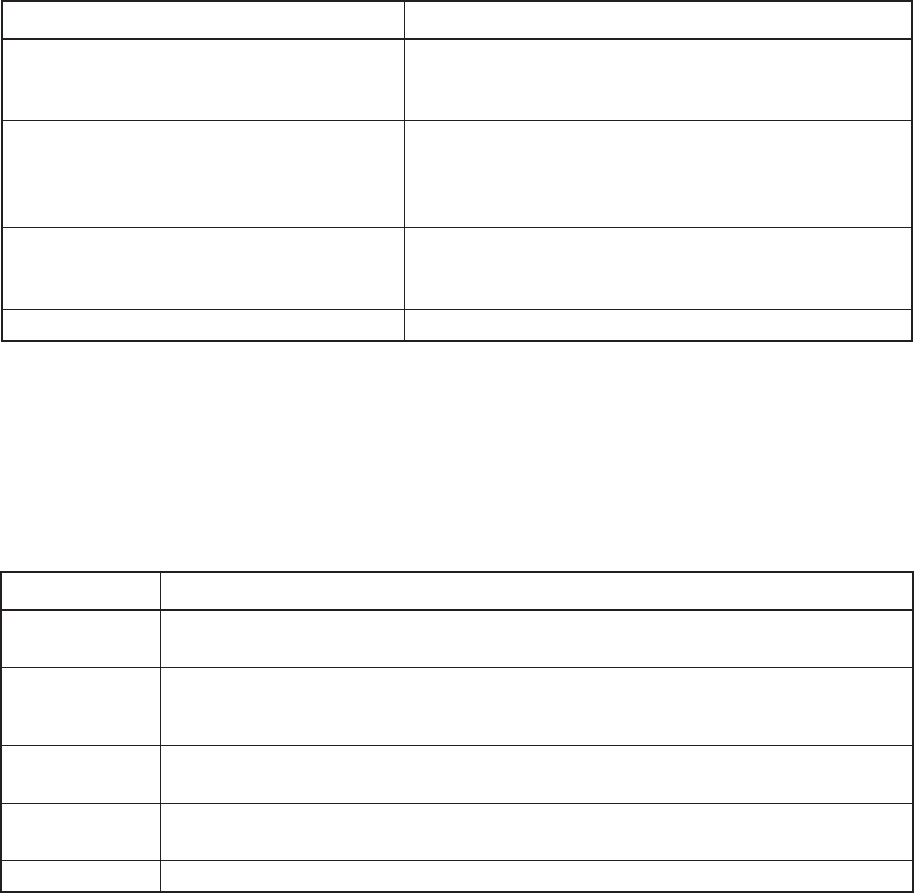
Table 6-1. Contents of Parameter Types
Parameter type Description
<Numeric> Represents decimal numbers. A <CHARACTER PRO-
<DECIMAL NUMERIC PROGRAM DATA> GRAM> item, such as MINimum or MAXimum, is
included in a special numeric format.
<Boolean> Represents a theoretical value. OFF or 0 corresponds to
<BOOLEAN PROGRAM DATA> FALSE, and ON or 1 corresponds to TRUE. When 0,1 or
(defined by SCPI) OFF, ON are used for setting, queries return 1 or 0, never
ON or OFF.
<Character> Represents a character data. It is possible to express a short
<CHARACTER PROGRAM DATA> character string corresponding to the setting contents. Both
long and short forms can be used.
<Non> Non parameter
6.2.7 Unit
The table below shows the unit types employed for this instrument.
In this manual, these unit types are written in lower-case alphabetical characters between brackets < >.
Table 6-2. Contents of Unit Types
Unit type Description
<Freq term> At frequency and FM deviation setting, four units can be use: “Hz”, “kHz”, “MHz”,
“GHz”. Omission of the unit symbol is regarded as “Hz”.
<Ampl term> At RF output level and AF output level setting, five units can be use: “dB”, “dBm”,
“dBu”, “V”, “mV”, “uV”. Omission of the unit symbol is regard is regard as “dBm” or
“V”.
<AM term> At AM depth setting, the unit must be “%” or “PCT”. Omission of the unit symbol is
regard as “%”.
<Time term> At sweep time setting, three units can be use: “s”, “ms”, “us”. Omission of the unit
symbol is regard as “s”.
<Non term> Non unit.


















