NI-DAQ Function Reference Chapter 6
PC-OPDIO-16 User Manual 6-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Primary Types
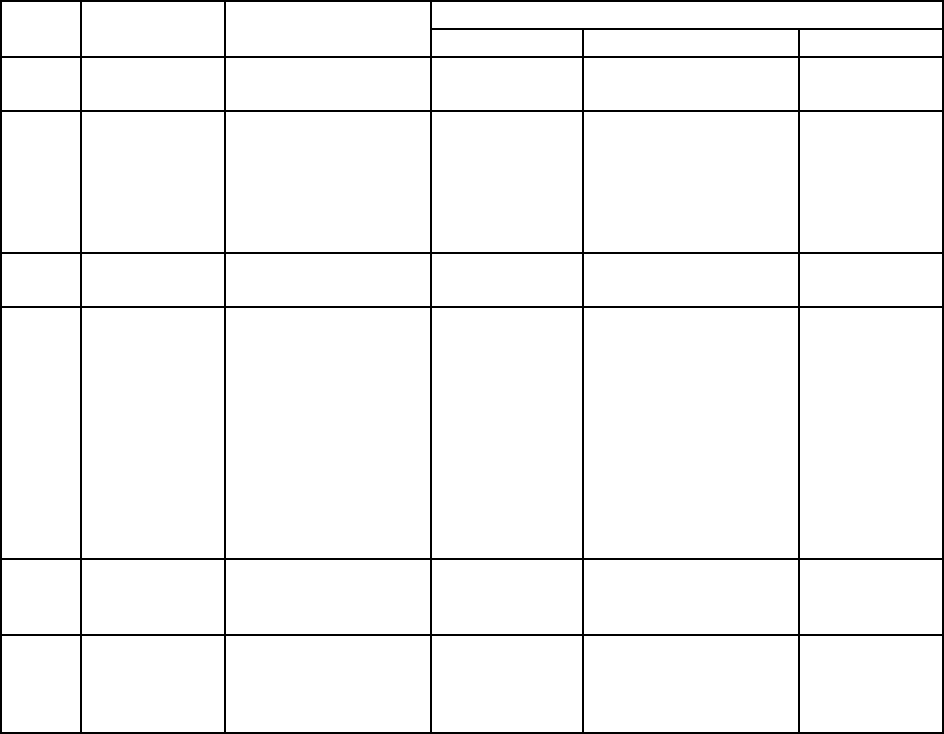
Table 6-2 shows the primary type names and their ranges.
Table 6-2. Primary Type Names
Type Description
Range Type
Name
C BASIC Pascal
I16 16-bit signed
integer
-32,768 to 32,767 short Integer (for example:
deviceNum%)
Integer
U16 16-bit unsigned
integer
0 to 65,535 unsigned
short
Not supported by
BASIC. For functions
that require unsigned
integers, use the signed
integer type instead.
See the I16 description.
Word
I32 32-bit signed
integer
-2,147,483,648 to
2,147,483,647
long Long integer (for
example: count&)
Longint
U32 32-bit unsigned
integer
0 to 4,294,967,295 unsigned
long
Not supported by
BASIC. For functions
that require unsigned
long integers, use the
signed long integer type
instead. See the I32
description.
Not supported
by Pascal. For
functions that
require
unsigned long
integers, use
the signed long
integer type
instead. See
the I32
description.
F32 32-bit single-
precision
floating point
-3.402823 x 10
38
to
3.402823 x 10
38
float Single-precision floating
point (for example:
num!)
Single
F64 64-bit double-
precision
floating point
-1.797683134862315 x
10
308
to
1.797683134862315 x
10
308
double Double-precision
floating point (for
example: voltage#)
Double
Programming Language Considerations
Apart from the data type differences, there are a few language-dependent considerations you
need to be aware of when you use the NI-DAQ API. Please read the following sections that
apply to your programming language.
Note: Be sure to include the NI-DAQ function prototypes by including the appropriate
NI-DAQ header file in your source code.


















