8-2 AC OUTPUT MEASURING
;a LOA;
TOACd/LE+@ $))
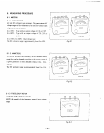
Use a circuit like the one shown in Fig. 8-7 for measuring XC output. A hot plate or lamp Lvith a power factor of 1 .O ma>-
be used as a load. Adjust the load and rpm. and check that the voltage range 1s as
specified in Table 5-1 at the rated amperage
and rated rpm
I
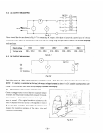
Rated voltage
1lOV
120v
220v 230V ’
240V
I
Voltage range
108 - 115V
118 - 125V 218 - 225V
228 - 235V
238 - 245V
I
Table 8- 1
8-3 DC OUTPUT MEASURING
Fig. 8-8
Switch the powr on. Khen 1.45R resistance is attached as a load.
check that the voltage is within the 13 to 1 IL7 range.
NOTE:
If a battery is connected as the load, the output voltage increases by about 7 TO ZV, possibly causing battery over-
charge. Control battery liquid level during charging to prevent overcharging.
8-4 MEASURING INSULATION RESISTANCE
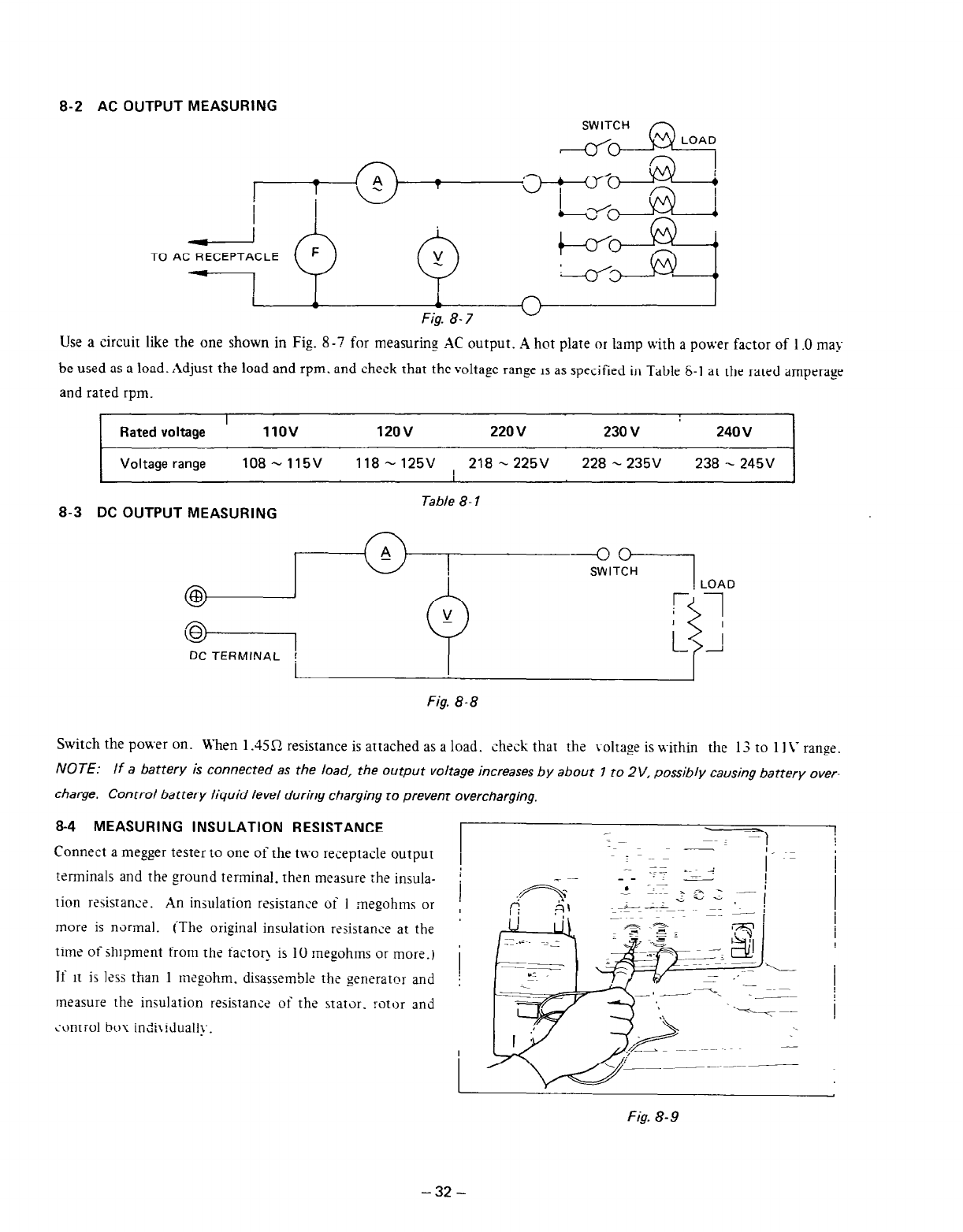
Connect a meger tester to one of the two receptacle output
terminals and the ground terminal. then measure rhe insula-
tion rssistanx. An insulation resistance of 1 megohms or
more is nxmal. (The original insulation resistance at the
time oishlpment from tht factor! is 10 megohms or more.)
Ji it is I?ss than 1 mqohm. disassembl? the generatnr and
measure the insulation resistance of the statOr. rotor and
cant;01 bc!x indi\!dual!~-.
I
I
I
1
. .
Fig. 8-9
-32-