SECTION 4.4
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
PART 4
DC CONTROL
3. Attach the spark plug lead to the spark tester terminal.
4. Crank the engine while observing the spark tester. If
spark jumps the tester gap, you may assume the engine
ignition system is operating satisfactorily.
NOTE:
The
engine
flywheel
must
rotate
at
350
rpm
(or
higher)
to
obtain
a
good
test
of
the
solid
state
ignition
system.
To determine if an engine miss is ignition related,
connect the spark tester in series with the spark plug
wire and the spark plug (Figure 21). Then, crank and
start the engine. A spark miss will be readily
apparent. If spark jumps the spark tester gap
regularly but the engine miss continues, the problem
is in the spark plug or in the fuel system.
NOTE:
A
sheared
flywheel
key
may
change
ignition
timing
but
sparking
will
still
occur
across
the
spark
tester
gap.
Figure 21. Checking Engine Miss
RESULTS:
1. If no spark or very weak spark occurs, go to Test 58.
2. If sparking occurs but engine still won't start, go to
Test 56.
3. When checking for engine miss, if sparking occurs at
regular intervals but engine miss continues, go to Test 16.
4. When checking for engine miss, if a spark miss is
readily apparent, go to Test 59.
TEST
56
-
CHECK
SPARK
PLUGS
DISCUSSION:
If the engine will not start and Test 55 indicated good
ignition spark, perhaps the spark plug(s) are fouled or
otherwise damaged. Engine miss may also be caused
by defective spark plug(s).
PROCEDURE:
1. Remove spark plugs and clean with a penknife or use a
wire brush and solvent.
2. Replace any spark plug having burned electrodes or
cracked porcelain.
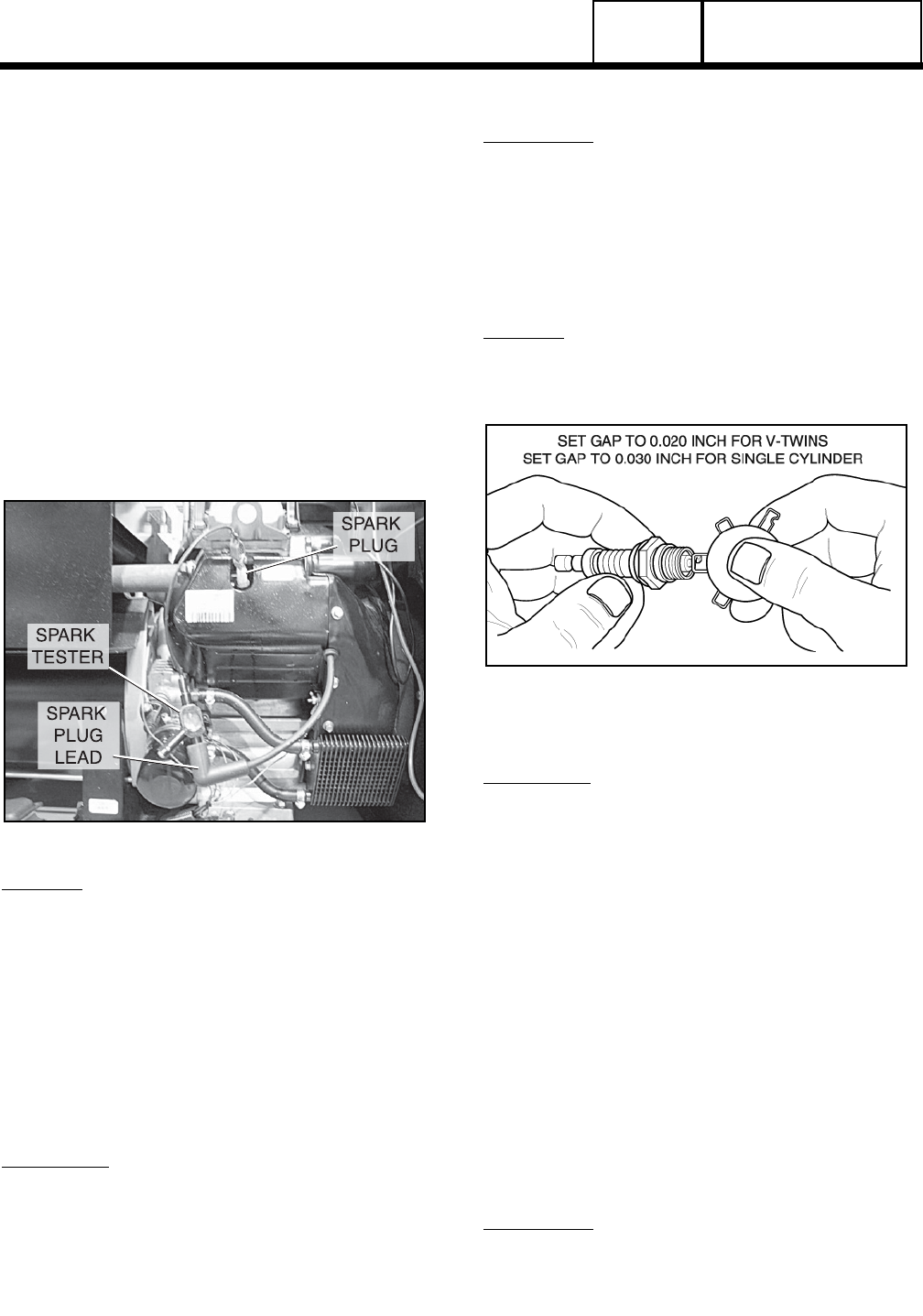
3. Set gap on new or used spark plugs to 0.030 inch for
single cylinder engines and 0.020 inch for v-twin engines.
RESULTS:
1. Clean, re-gap or replace spark plugs as necessary.
2. If spark plugs are good, go to Test 62.
Figure 22. Checking Spark Plug Gap
TEST
57-
CHECK
ENGINE
COMPRESSION
DISCUSSION:
Lost or reduced engine compression can result in (a)
failure of the engine to start, or (b) rough operation.
One or more of the following will usually cause loss of
compression:
❏Blown or leaking cylinder head gasket.
❏Improperly seated or sticking-valves.
❏Worn Piston rings or cylinder. (This will also result
in high oil consumption).
NOTE:
For
the
single
cylinder
engine,
the
minimum
allowable
compression
pressure
for
a
cold
engine
is
60
psi.
NOTE:
It
is
extremely
difficult
to
obtain
an
accurate
compression
reading
without
special
equipment.
For
that
reason,
compression
values
are
not
published
for
the
V-TTwin
engine.
Testing
has
proven
that
an
accurate
compression
indication
can
be
obtained
using
the
following
method.
PROCEDURE:
Page 4.4-12


















