2009 Portable Spa
LTR20091000, Rev. A
Clear Water Plan
www.calspas.com
21
Testing and Adjusting Spa Water
You have two types of testing methods to choose from:
The • reagent test kit is a method which provides a high level of accuracy. It is available in either liquid
or tablet form.
Test strips • are a convenient testing method commonly used by spa owners.
Balancing the pH
The pH level is the measure of the balance between
acidity and alkalinity.
If the pH is too low, it can cause corrosion of metal
xtures and the heating element. Low pH can be
corrected by adding pH-Alkalinity Up.
If the pH is too high, it can cause scaling by allowing
metals or minerals to form deposits and stain spa
surfaces. High pH can be corrected by adding pH-
Alkalinity Down.
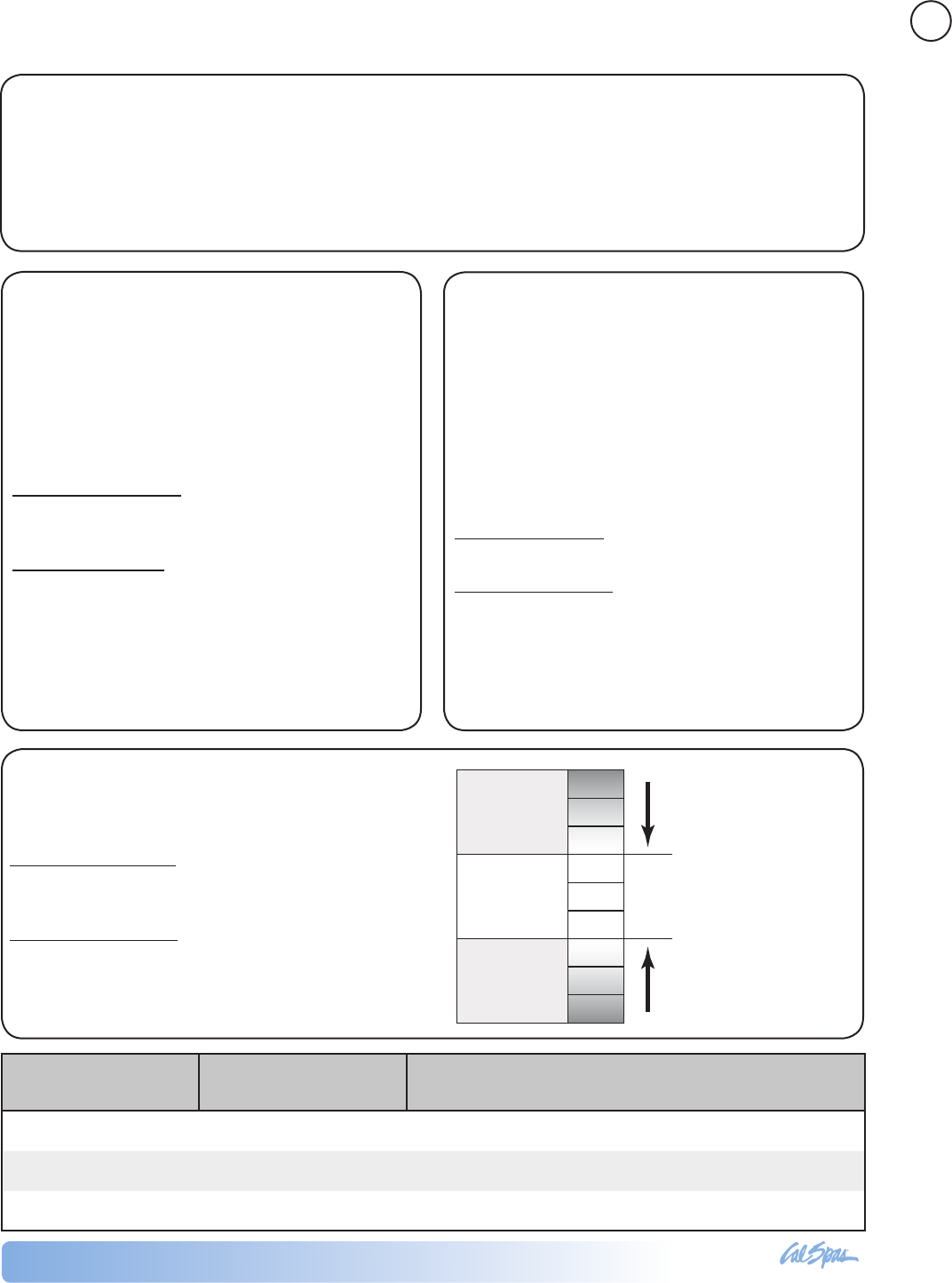
8.2
8.0
7.8
7.6
7.4
7.2
7.0
6.8
6.6
Too alkaline,
causes scaling
Ideal balance
Too acidic,
causes corrosion
Need to lower the pH level
Need to raise the pH level
Balancing the Total Alkalinity
Total alkalinity (TA) is the measure of the total
levels of carbonates, bicarbonates, hydroxides, and
other alkaline substances in the water. TA can be
considered a “pH buffer”. It is the measure of the
ability of the water to resist changes in pH level.
The recommended total alkalinity is 80 - 120
ppm.
If the TA is too low, the pH level will uctuate
widely from high to low. Low TA can be corrected
by adding Cal Spas “pH-Alkalinity Up”.
If the TA is too high, the pH level will tend to be too
high and may be difcult to bring down. High TA
can be corrected by adding Cal Spas “pH-Alkalinity
Down”.
When the TA is balanced, it normally remains
stable, although adding water with high or low
alkalinity will raise or lower the TA level.
Balancing the Calcium Hardness
Calcium hardness (CH) is a measure of the total
amount of dissolved calcium in the water. Calcium
helps control the corrosive nature of the spa’s water
and is why soft water is not recommended. The low
calcium content of soft water is very corrosive to
the equipment and can cause staining of the spa
shell.
The recommended calcium hardness is 150
- 200 ppm.
If the CH is too low, add Cal Spas “Liquid Hardness
Increaser”.
If the CH is too high, dilute the spa water with soft
water or, if this is not available, add Cal Spas “Stain
and Scale Defense”.
When the CH is balanced, it normally remains
stable, although adding soft water or very hard
water will raise or lower the CH level.
Testing For: Ideal Range (ppm) Chemicals To Use:
Minimum Maximum To Raise To Lower
Total Alkalinity 80 120 pH-Alkalinity Up pH-Alkaliity Down
Calcium Hardness 150 200 Liquid Hardness Increaser Stain and Scale Defense
pH 7.4 7.6 pH-Alkalinity Up pH-Alkaliity Down


















