8
Repeatability and linearity
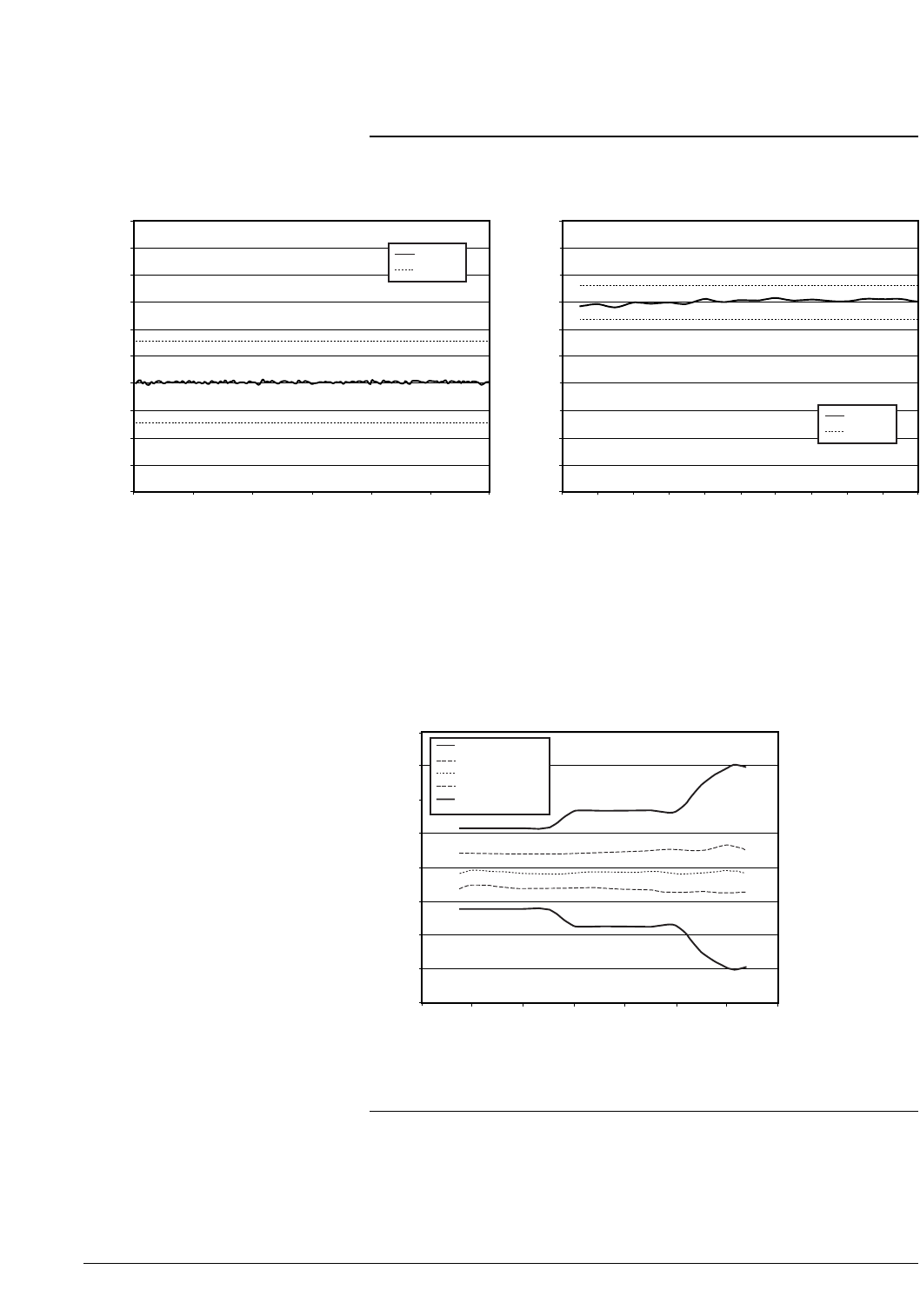
Relative level accuracy measures the accuracy of a step change from any power level to any
other power level. This is useful for large changes (i.e. 5 dB steps).
1
Specifications for Frequency and Power Characteristics
1. Repeatability and relative level accuracy are typical for all frequency ranges.
Repeatability
1900 MHz CW, 5 dBm, attenuator hold On, ALC On
0
20 40
60
80
100
120
Elapsed time (minutes)
Powererror (dB)
0.1
0.09
0.08
0.07
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.01
0
Typical unit
Limits
Repeatability
1900 MHz CW, 5 dBm, attenuator hold Off, ALC Off
0
1
Elapsed time (minutes)
Power error (dB)
0.5
0.45
0.4
0.35
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.10
0.05
0
2 3 54 6 71 8 910
Typical unit
Limits
Relative level accuracy
Initial power 7 dBm
0
-20 -40 -60
Final power (dBm)
Power error (dB)
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
-0.4
-140
-120-80 -100
Lower limit
Lower STD deviation
Mean
Upper STD deviation
Upper limit
Repeatability measures the ability of the instrument to return to a given power setting after a
random excursion to any other frequency and power setting. It is a relative measurement that
reflects the difference in dB between the maximum and minimum power readings for a given
setting over a specific time interval. It should not be confused with absolute power accuracy,
which is measured in dBm.
1


















