TP-5700 7/93 25Section 6 Fuel Systems
Section 6 Fuel Systems
When planning an installation, check state and local
regulations regarding fuel storage and handling. Piping and
fuel system components must conform to these
regulations.
6.1 Diesel Fuel Systems
Since diesel fuel is less volatile than gas or gasoline, it
may be considered safer fuel from the standpoint of
storage and handling. This is often reflected in less
stringent regulations for placement of tanks. In some
locations, main tanks of considerable size are permitted
inside the building or enclosure; however, local
regulations must be checked before planning the
installation.
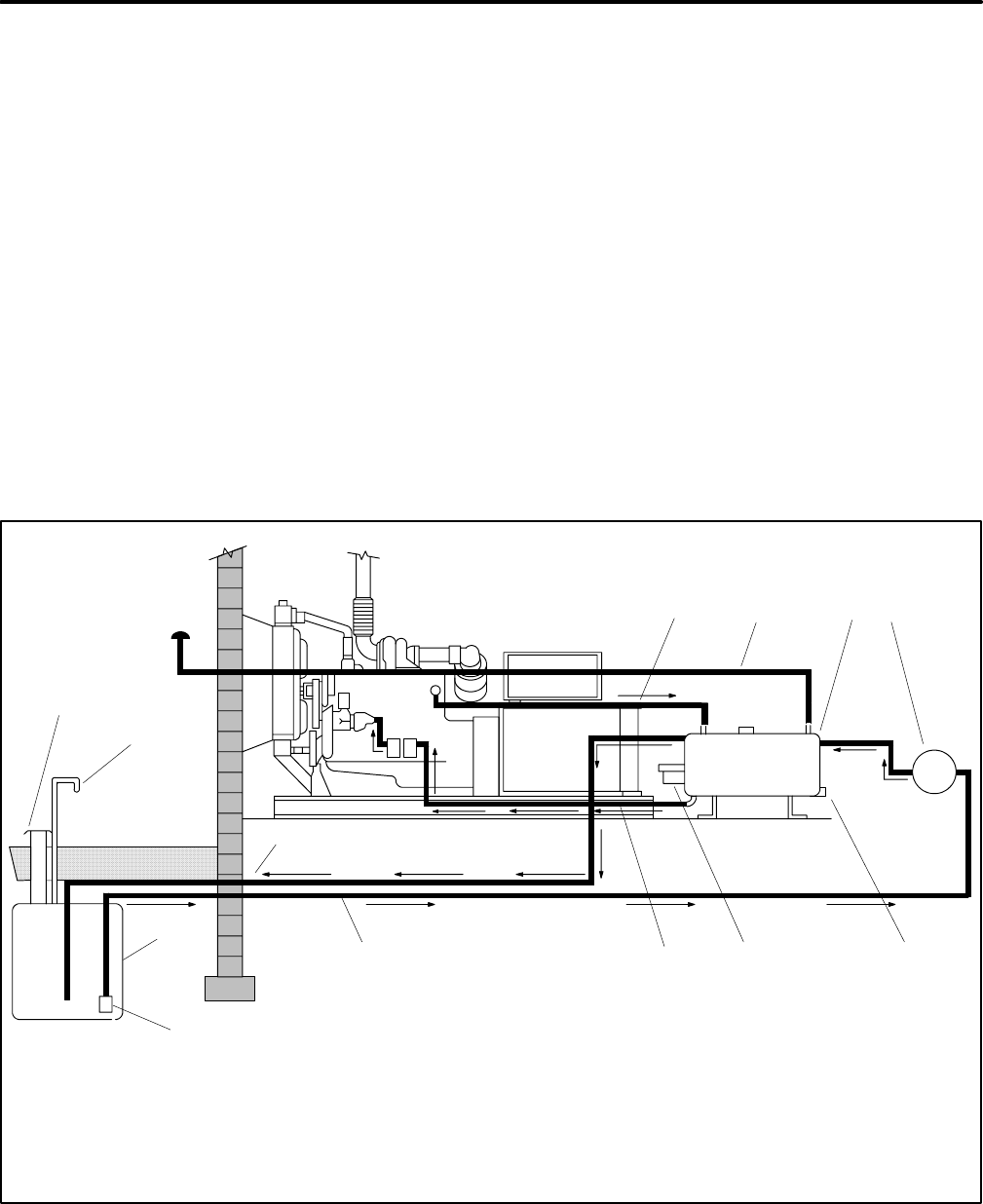
The main components of a typical diesel fuel system are
a main fuel storage tank, fuel lines, transfer tank, and
auxiliary fuel pump. See Figure 6-1.
Fuel storage tanks may be located above ground
indoors or outdoors, or buried underground.
“Base-mounted” or “subbase” tanks are commonly
used. This is a tank that is contained in a base that the
generator is mounted on. See Figure 6-2.
Fuel filters and sediment drains must be easily
accessible for regular and frequent service. Cleanliness
of the fuel is especially important on diesel engines
which have easily clogged, precision fuel injectors and
pumps. Black iron pipe or steel tubing must be used for
diesel fuel systems—galvanized tanks and piping must
not be used since the diesel fuel will react chemically
with themto produce flaking whichwill quicklyclog filters
or causes failure ofthe fuel pump or injectors. Allflexible
lines must be of the type approved for diesel fuels.
12
11
9
13
1 2 3 4
568
10
TP-5700-6
1. Injector return line
2. Day tank vent
3. Day tank
4. Auxiliary fuel pump
5. Tank drain
6. Electric fuel level control switch
7. Fuel supply line from day tank to engine connection
8. Fuel supply line from main fuel tank to day tank
9. Overflow line
10. Foot valve
11. Main fuel storage tank
12. Fuel tank vent
13. Tank filling inlet
7
Figure 6-1 Diesel Fuel System