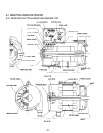
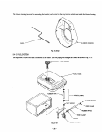
7. RANGE of APPLICATIONS
Generally, the rated power of an electrical appliance often refers to the amount of work that can be done by it. The electric
power required for operating an electrical appliance is not necessarily equal to the amount of work that can be done by it.
Electrical products generally have a label showing their rated voltage, frequency, and power consumption (input power). The
power consumption of an electrical products is the power necessary for using it. When using a generator for operatiig an
electrical product, however, the power factor and starting current must also be taken into consideration.
Determine the required capacity of your generator from the power required for operating electrical products that are class&
fied as follows:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Incandescent lamps, hot plates, etc. with a power factor of 1 .O
Total power consumption must be equal to or less than the rated output of the generator.
Example: A generator with a rated output power of 1000 W can light ten 100 W lamps.
Fluorescent lamps, mercury lamps, etc. with a smaller power factor
Select a generator with a rated output equivalent to 1.2 to 2 times the power consumption of the load.
Example: A generator with a capacity of 100 W to 160 W is necessary for lighting a 80 W fluorescent lamp. A generator
with a rated output of 1000 W can light 6 to 10 40 W fluorescent lamps.
NOTE: Wattage of the fluorescent lamp generally does not indicate the power consumption but indicates the ou@ut of
the lamp. Therefore, if the fluorescent lamp has no s,oecial indication as to the power conwmption or input power,
efficiency should be taken into accounts as explained in
Item
5 on the folio wingpage.
Electric tools, etc. that are driven by a motor
Power 1.2 to 3 times the power consumption of a motor-driven tool is required for starting so select a generator with a
maximum output 1.2 to 3 times the power consumption of the load.
Example: A 300 W motor-driven drill requires a generator with a maximum output of 400 to 900 W or more.
Water pumps, compressors, etc. that are driven by a motor which is loaded at starting
3 to 5 times the power consumption of the load is necessary for starting so select a generator with a maximum output
3 to 5 times its power consumption.
Example: A water pump with a power consumption of 400 W requires a generator with a maximum output of 1200 to
2000 W or more.
NOTE 1: Motor-driven products mentioned in
Items 3
and 4
required the
aforementioned generator
capacities only
when starting their
mOtOfs.
Once their motors are started, the products consume only about 7.2 to 2 times &eir rated
power consumption
SO
that the excess power generated by the generator can be used for other electrical
appliances.
NOTE 2:
Motor-driven producrs mentioned in Items 3 and 4 vary in their required motor starthg power
depemfing on
the kind of motor and
start-up
load. If it is difficult to determine the optimum generator capacity, select a
genemtor
with a larger capacity.
- 29 -