26
RC5010 & RC6010 (540 RPM) and RCM5010 & RCM6010 (1000 RPM) Rotary Cutters 318-128M 8/28/08
Land Pride
Section 5: Maintenance & Lubrication
Table of Contents
Drivelines With Slip Clutches
!
CAUTION!
Engage parking brake, disengage PTO, shut off tractor, and
remove key before working on or around the driveline and/or
slip clutch.
!
CAUTION!
Slip clutches that have been in use or have been slipped for only
two or three seconds during run-in may be too hot to touch.
Allow a hot clutch to cool before working on it.
Cutter drive components are protected from shock loads
by a friction slip clutch. The clutch must be capable of
slippage during operation to protect the gearbox,
driveline and other drive train parts.
Friction clutches should be “run-in” prior to initial
operation and after long periods of inactivity to remove
any oxidation that may have accumulated on the friction
surfaces. Repeat “run-in” instructions at the beginning of
each season and when moisture and/or condensation
seizes the inner friction plates.
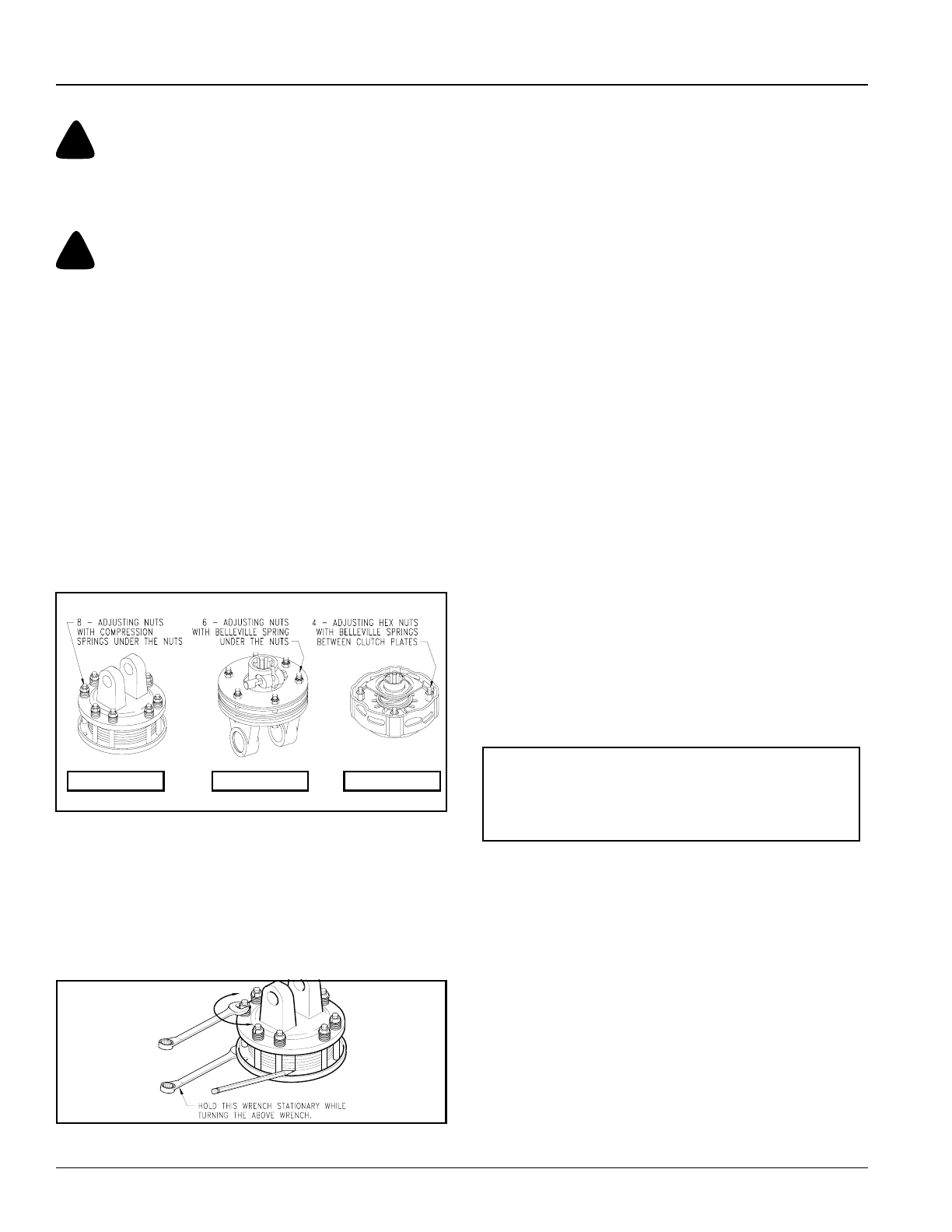
Refer to Figure 5-2 to determine which friction clutch
your cutter has. Follow “run-in” instructions on the
following pages for your specific clutch type.
Clutch Types
Figure 5-2
Type A Clutches
Clutch Run-In
Refer to Figure 5-3:
1. Using a pencil or other marker, scribe a line across the
exposed edges of the clutch plates and friction disks.
Type A Clutch Run-In
Figure 5-3
Type A Clutch Type B Clutch
23560
Type C Clutch
13693
2. Carefully loosen each of the 8 spring retainer nuts by
exactly 2 revolutions. It will be necessary to hold hex
end of retainer bolt in order to count the exact
number of revolutions.
3. Make sure the area is clear of all bystanders and
machine is safe to operate.
4. Start tractor and engage PTO drive for 2-3 seconds
to permit slippage of the clutch surfaces. Disengage
PTO, then re-engage a second time for 2-3 seconds.
Disengage PTO, shut off tractor and remove key.
Wait for all components to stop before dismounting
from tractor.
5. Inspect clutch and ensure that the scribed markings
made on the clutch plates have changed position.
Slippage has not occurred if any two marks on the
friction disk and plate are still aligned. A clutch that
has not slipped must be disassembled to separate
the friction disk plates. See “Clutch Disassembly,
Inspection & Assembly” below.
6. Tighten each of the 8 spring retainer nuts on the
clutch housing exactly 2 revolutions to restore clutch
to original setting pressure.
7. Allow clutch to cool to ambient temperature before
operating again. Clutch is now ready for use.
8. The clutch should be checked during the first hour of
cutting and periodically each week. An additional set
of scribe marks can be added to check for slippage.
See Figure 5-5 to adjust spring length.
Clutch Disassembly, Inspection & Assembly
Refer to Figure 5-4:
If clutch run-in procedure above indicated that one or more
friction disks did not slip, then the clutch must be
disassembled to separate the friction disks.
Disassembly
Disassembly of clutch is simply a matter of first removing
spring retainer nuts (#1), springs (#2) and bolts (#3) from
the assembly. Each friction disk (#4) must then be
separated from the metal surface adjacent to it.
Inspection
Inspect all parts for excessive wear and condition. Clean
all parts that do not require replacement.The original
friction disk thickness is 1/8" (3.2mm) and should be
replaced if thickness falls below 3/64" (1.1mm). If
clutches have been slipped to the point of “smoking”, the
friction disks may be damaged and should be replaced.
Heat build-up may also affect the yoke joints.
Assembly
Reassemble each friction disk (#4) next to the metal
plate it was separated from. Install bolts (#3) through the
end plates and intermediate plates as shown. Place
springs (#2) over the bolts and secure with nuts (#1).
IMPORTANT: Not all Type A clutch components are
arranged as illustrated in Figure 5-4. Also some
have more components than others. Be sure to keep
track of order and orientation of your clutch
components during disassembly.


















