PAGE 40 — INDUSTRIAL GENERATOR SETS — APPLICATION & INSTALLATION MANUAL — REV. #4 (09/07/07)
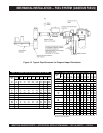
MECHANICAL INSTALLATION — FUEL SYSTEM (GASEOUS FUELS)
Gaseous Fuels
Some MQ Power Industrial generator sets may utilize
gaseous fuels such as Pipeline natural gas or Liquid
Petroleum Gas (LPG). Regardless of the fuel used, the
primary factors in successful installation and operation of a
gas fuel system are:
The gas supplied to the generator set must be of
acceptable quality.
The gas supply pressure must be measured to ensure
that the gas supply at the generator set, not just at the
source, is of proper pressure must be available while the
generator is running at full load.
The gas must be supplied to the genset in sufficient
volume to support proper operation.
Gaseous fuels are actually a mixture of several different
hydrocarbon gases and various contaminants, some of
which are potentially damaging to an engine over time.
The quality of the fuel is based on the amount of energy
per unit volume in the fuel and the amount of contaminants
in the fuel. Most gaseous fuel suppliers can provide a
fuel analysis that describes the chemical makeup of the
fuel that is to be provide to insure that the fuel is usable
for a specific application, and also to verify that the BTU
content of the fuel is sufficient to provide necessary kW
output of the genset.
Energy Content
One of the most important characteristics of gaseous
fuel used in a generator set is the heat value of the fuel.
The value of a fuel describes how much energy is stored
in a specific volume of the fuel. Gaseous fuel has a low
heat value (LHV) and a high heat value (HHV). The low
heat value is the heat available to do work in an engine
after the water in the fuel is vaporized. If the low heat
value of the fuel is too low (generally below 905 BTU/ft
3
)
the engine will not be able to maintain full output power
and may not produce rated power at standard ambient
temperature conditions.
Pipeline Natural Gas
The most common gaseous fuel for generator sets is
called
Pipeline natural gas
. In the United States, "dry
pipeline natural gas" has specific qualities based on
federal requirements. U.S. pipeline gas is a mixture
composed of approximately 98% methane and ethane
with the other 2% being hydrocarbons such as propane
and butane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
"Dry" means that is free of liquid hydrocarbons such as
gasoline, but NOT that it is free of water vapor.
Field Gas
The composition of
Field natural gas
varies considerably
by region and continent. Careful analysis is necessary
prior to using field natural gas in an engine because in
can contain heavier hydrocarbon gases which may require
derating of the output of the engine. Field natural gas
may also contain other contaminants such as sulfur.
Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG)
Liquid Petroleum Gas is available in two grades,
commercial and special duty. Commercial propane is
used where high volatility is required. Special duty
propane (also called HD5) is a mixture of 95% propane
and other gases such as butane that allows better engine
performance due to the reduction pre-ignition due to
reduced volatility. Special duty propane fuel should meet
the ASTM D 1835 specifications for special duty propane.
BTU Content
The total BTU content of the fuel will determine the rating of
the generator set when using fuel of a specific compostion.
If any component of the fuel has more than the specific
value allowed, derating will be required. Consult MQ Power
for fuel derating instructions.
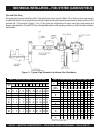
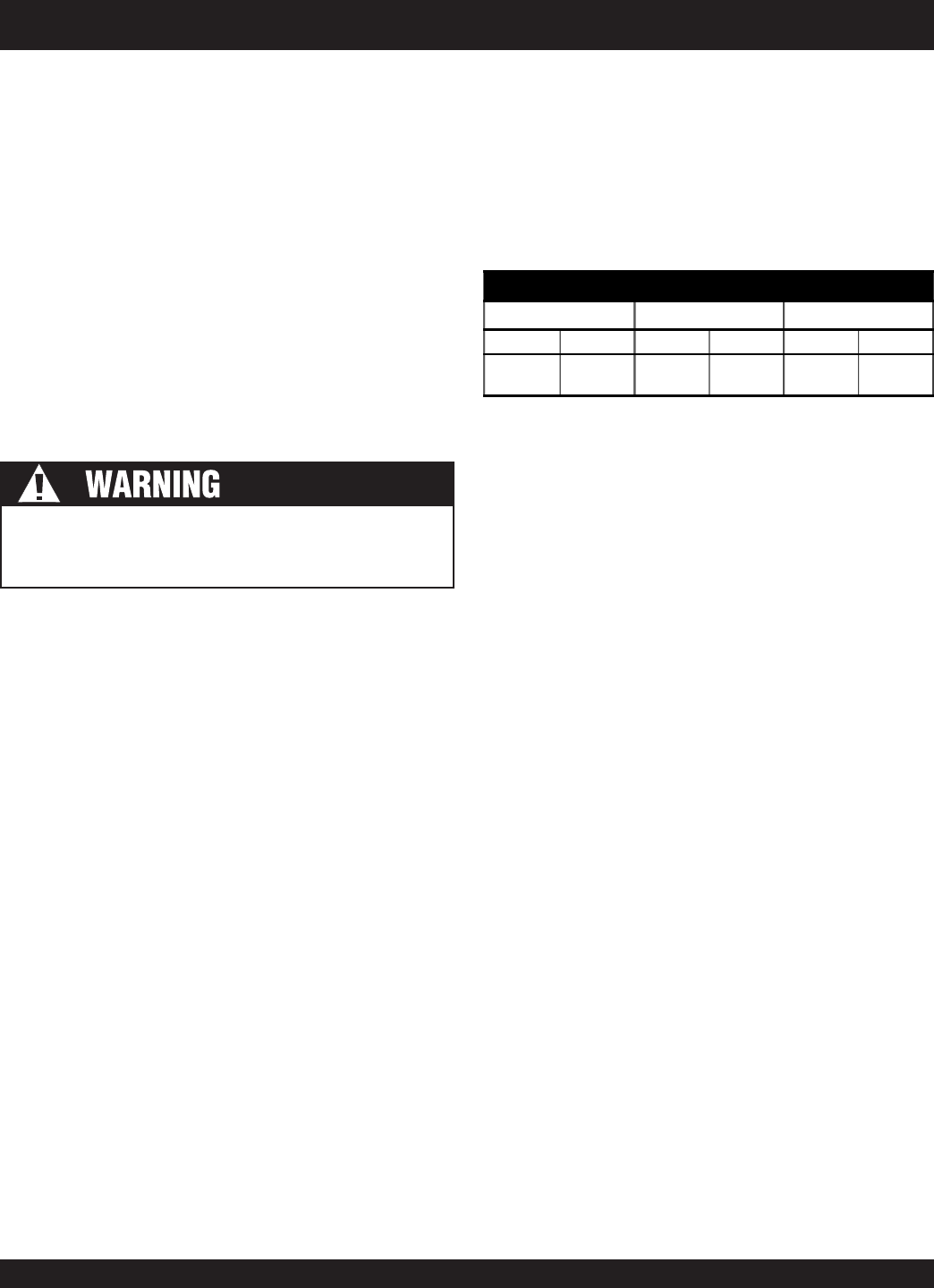
TABLE 11. TYPICAL BTU CONTENT OF GASEOUS FUEL
DRY PIPELINE GAS FIELD GAS LPG
LHV HHV LHV HHV LHV HHV
936
BTU/ft
3
1,038
BTU/ft
3
1,203
BTU/ft
3
1,325
BTU/ft
3
2,353
BTU/ft
3
2,557
BTU/ft
3
Failure to meet the minimum requirements in these areas will
result in the inability of the generator set to operate or carry
rated load and will induce poor performance.