– 11 –
• The Moon: A veritable treasury of craters, mountain ranges and fault lines. The best contrast for viewing
the Moon is during its crescent phase. The contrast during the full Moon phase is low due to the angle
of illumination.
• Deep-Space: Nebulae, galaxies, multiple star systems, star clusters–hundreds of such objects are
visible through the Model 4500.
F. Using Setting Circles
Setting circles of the polar aligned equatorial mount can facilitate the location of faint celestial objects not
easily found by direct visual observation. To use the setting circles, follow this procedure:
• Use a star chart or star atlas, and look up the celestial coordinates, Right Ascension and Declination
(R.A. and Dec.), of an easy-to-find bright star that is within the general vicinity of the faint object you
wish to locate.
• Center the determined bright star in the telescope’s field of view.
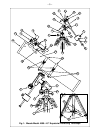
• Manually turn the R.A. setting circle (27) to read the R.A. of the object now in the telescope’s eyepiece.
• The setting circles are now calibrated (the Dec. setting circle (28) is factory calibrated). To locate a
nearby faint object using the setting circles determine the faint object’s celestial coordinates from a star
chart, and move the telescope in R.A. and Declination until the setting circles read the R.A. and Dec. of
the object you are attempting to locate. If the above procedure has been carefully performed, the faint
object will now be in the field of a low power eyepiece.
• The R.A. Setting Circle must be manually re-calibrated on the current Right Ascension of a star every
time the telescope is set up, and reset to the centered object’s R.A. coordinate before moving to a new
R.A. coordinate setting. The R.A. Setting Circle has two sets of numbers, the inner set is for Southern
hemisphere use while the outer set of numbers (the set closest to the R.A. gear), is for use by observers
located North of the Earth’s equator (e.g. in North America).
G. Calculating Power
The power, or magnification of the telescope depends on two optical characteristics: the focal length of the
main telescope and the focal length of the eyepiece used during a particular observation. For example, the
focal length of the Model 4500 telescope is fixed at 910mm. To calculate the power in use with a particular
eyepiece, divide the focal length of the eyepiece into the focal length of the main telescope. For example,
using the MA25mm eyepiece supplied with the Model 4500, the power is calculated as follows:
Power =
910mm
= 36x
25mm
Meade Instruments manufactures several types of eyepiece designs that are available for your telescope.
The type of eyepiece (“MA” Modified Achromatic, “SP” Super Plössl, etc.) has no bearing on magnifying
power but does affect such optical characteristics as field of view, flatness of field, eye-relief, and color
correction.
The maximum practical magnification is determined by the nature of the object being observed and, most
importantly, by the prevailing atmospheric conditions. Under very steady atmospheric “seeing,” the Model
4500 may be used at powers up to about 228x on astronomical objects. Generally, however, lower powers
of perhaps 75x to 175x will be the maximum permissible, consistent with high image resolution. When
unsteady air conditions prevail (as witnessed by rapid “twinkling” of the stars), extremely high-power
eyepieces result in “empty magnification,” where the object detail observed is actually diminished
by the
excessive power.
Assorted eyepieces are available both to increase and decrease the operating eyepiece power of the
telescope. If the Model 4500 is used on a regular basis, a selection of four to five eyepieces is recom-
mended. For example, an eyepiece assortment of focal lengths 40mm, 25mm*, 12.5mm, 9mm, and 6mm
yields a magnifying range of 22.5x, 36x, 72x, 101x, and 150x respectively. A high quality Barlow Lens, such
as the Meade #126 2x Telenegative Barlow Lens, serves to double the power of each of these eyepieces.
To use the Barlow Lens, insert the #126 unit into the telescope’s focuser first, followed by an eyepiece; the
power thus obtained is then double the power obtained when the eyepiece is used alone. For example, the
MA25mm eyepiece, when used in conjunction with the #126 2x Telenegative Barlow Lens yields 72x.