Cryptography Overview
56 RSA BSAFE Crypto-C Developer’s Guide
to reveal the contents of a digital envelope.
The main features of OAEP are redundancy and randomization. The redundancy feature
makes it difficult for an attacker to create a new derived message from an existing
ciphertext message. The recipient of a derived message checks the redundancy after
decrypting the message and rejects redundant messages. The PKCS #1 format has
only about 16 bits of redundancy, whereas OAEP formats have 64 to 160 bits of
redundancy.
The randomization feature makes each bit of the input to the public key operation
dependent on each bit of the message and on 64 to 160 bits of randomness. This makes
it difficult for chosen input attacks to work, and it causes ciphertext tampering to
change many bits in the decrypted message.
Together, redundancy and randomization create verifiable properties for securing
digital envelopes.
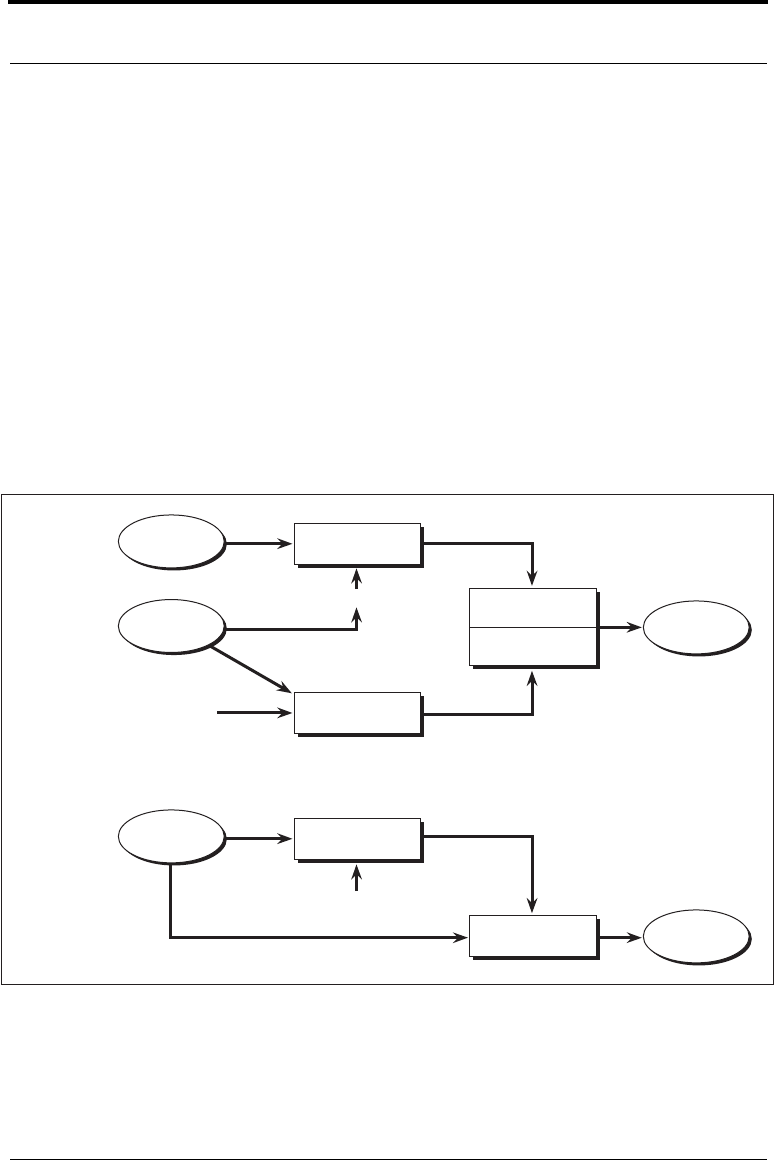
Figure 3-10 Digital Envelope
Message
Symmetric
Key Data
Recipient’s
Public Key
Public-Key
Encryption
Private Key
Digital
Envelope
Private-Key
Decryption
Encrypted
Message
Symmetric-Key
Encryption
Encrypted
Key
Symmetric-Key
Decryption
Data-Encrypting
Key
Encrypted
Message
Sealing
Operation
Envelope
Open
Operation
Message
Digital
Envelope
Encrypted
Key
Symmetric Key
