Generating Random Numbers
168 RSA BSAFE Crypto-C Developer’s Guide
predict or reproduce. Once you have seeded the random algorithm, the algorithm can
produce a sequence of random bytes; these bytes are “more random” and are
generated more quickly than the seed. See “Pseudo-Random Numbers and Seed
Generation” on page 92 for more information.
Before you get your seed, you need to set aside memory to hold it. In this example,
you will allocate 256 bytes for your seed:
Now get the random seed. The exact method you use to get the seed will depend on
your application and how the seed is generated. Here is a quick method for getting
keyboard input. This method is not recommended for an actual application; it is
supplied for illustrative purposes only:
Note: Another method for acquiring a seed would be to use a hardware random
number generator, if available, such as the Intel Random Number Generator
described in the Crypto-C Intel Security Hardware User’s Guide. However, even
if you have access to random numbers from hardware, you will still want to
have a fallback method of seed collection, in case the hardware random
number generator is not available or fails for some reason.
Here you are using a 256-byte buffer. When the space was allocated, the contents of
the buffer were simply whatever happened to be in that memory location at the time.
In this case, when you enter a seed at the keyboard (the
gets function), you overwrite
the first few bytes in the buffer, one byte for each keystroke. Now, the first bytes in the
buffer are the input from the keyboard; the rest of the 256 bytes are untouched.
Note: If you want to guarantee a repeatable seed (for example, if you are testing and
want to be able to reproduce your data), set the buffer with
T_memset.
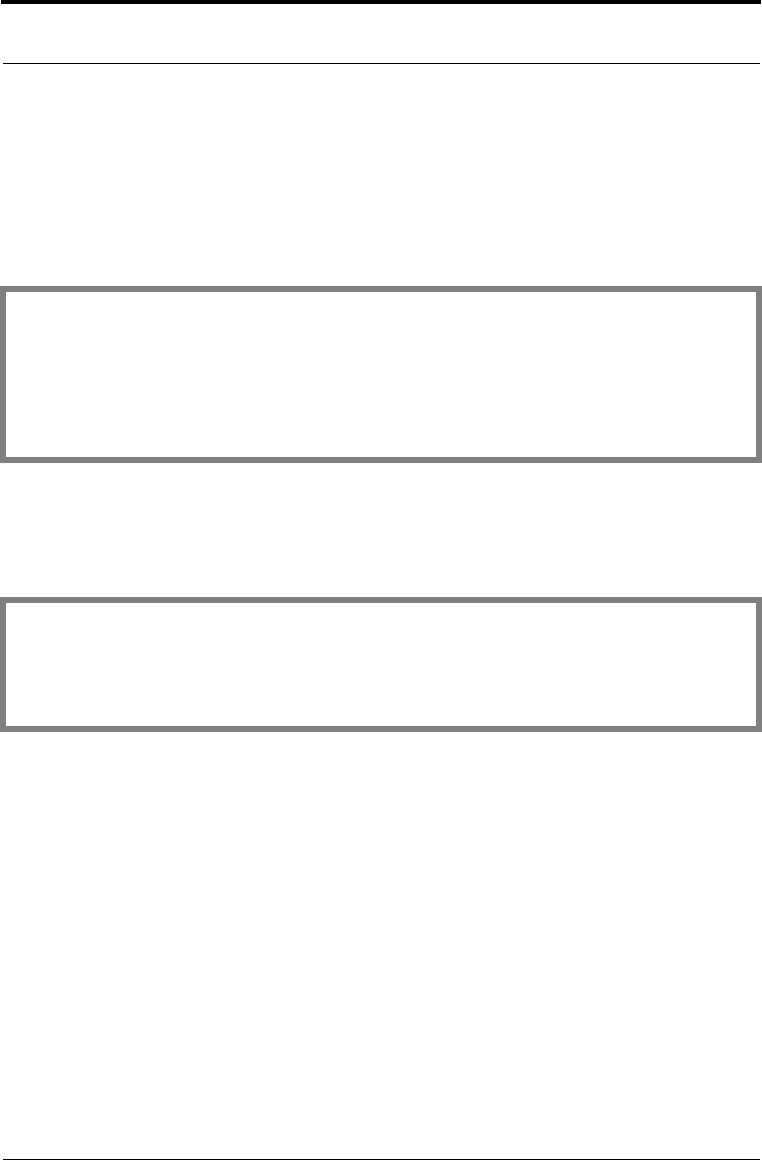
POINTER randomSeed = NULL_PTR;
unsigned int randomSeedLen;
randomSeedLen = 256;
randomSeed = T_malloc (randomSeedLen);
if ((status = (randomSeed == NULL_PTR)) != 0)
break;
puts (“Enter a random seed”);
if ((status =
(NULL_PTR ==
(unsigned char *)gets ((char *)randomSeed))) != 0)
break;
