CUTTING BLADES
10 – English
Abrasive blades
• The cutting material on abrasive blades consists of
grit bonded using an organic binder. ”Reinforced
blades” are made up of a fabric or fibre base that
prevents total breakage at maximum working speed if
the blade should be cracked or damaged.
• A cutting blade’s performance is determined by the
type and size of abrasive corn, and the type and
hardness of the bonding agent.
• Ensure the cutting blade is not cracked or damaged.
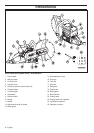
• Test the abrasive blade by hanging it on your finger
and tapping it lightly with a screwdriver or the like. If
the blade does not produce a resonant, ringing sound
it is damaged.
Abrasive blades for different materials
Diamond blades
General
• Diamond blades consist of a steel core provided with
segments that contain industrial diamonds.
• Diamond blades ensure lower costs per cutting
operation, fewer blade changes and a constant cutting
depth.
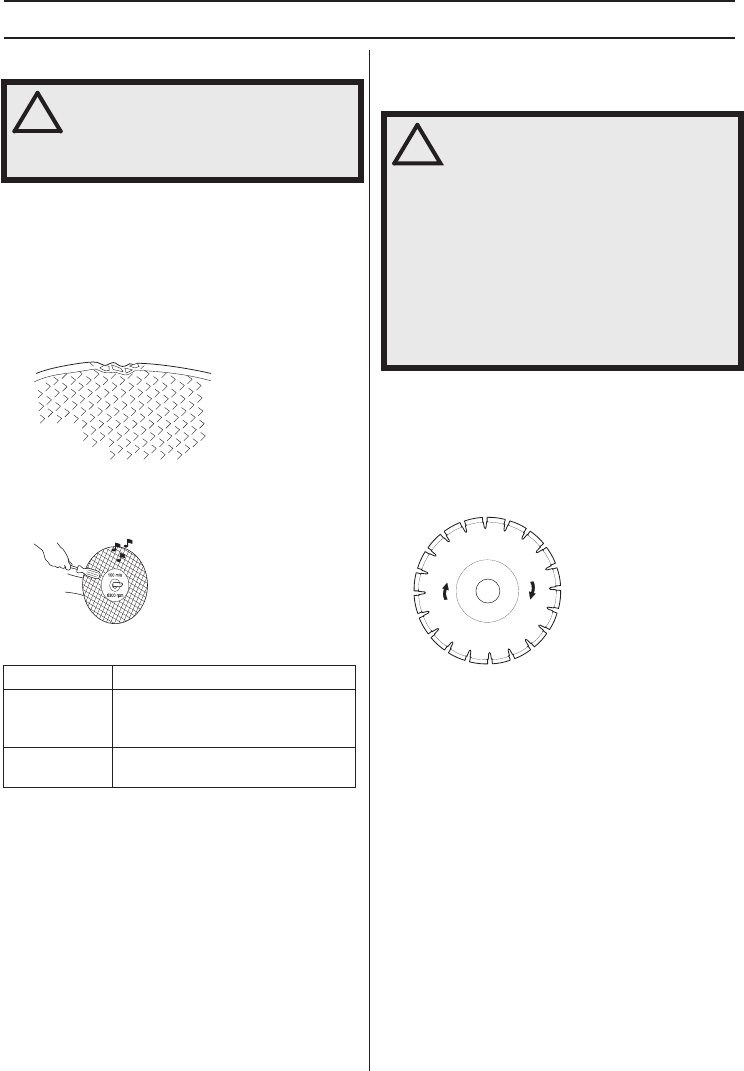
• When using diamond blades make sure that it rotates
in the direction indicated by the arrow on the blade.
Diamond blades for different materials
• Diamond blades are ideal for masonry, reinforced
concrete and other composite materials.
• Diamond blades are available in several hardness
classes.
• Special blades should be used when cutting metal.
Ask your dealer for help in choosing the right product.
Sharpening diamond blades
• Always use a sharp diamond blade.
• Diamond blades can become dull when the wrong
feeding pressure is used or when cutting certain
materials such as heavily reinforced concrete.
Working with a blunt diamond blade causes
overheating, which can result in the diamond
segments coming loose.
• Sharpen the blade by cutting in a soft material such as
sandstone or brick.
!
WARNING! Do not use abrasive blades
with water. The strength is impaired
when abrasive blades are exposed to
water or moisture, which results in an
increased risk of the blade breaking.
Blade type Material
Concrete blade
Concrete, asphalt, stone masonry,
cast iron, aluminium, copper, brass,
cables, rubber, plastic, etc.
Metal blade
Steel, steel alloys and other hard
metals.
!
WARNING! Never use a diamond blade to
cut plastic material. The heat produced
during cutting may melt the plastic and it
can stick to the cutting blade and cause a
kickback.
Diamond blades become very hot when
used. An overheated blade is a result of
improper use, and may cause
deformation of the blade, resulting in
damage and injuries.
Cutting metal generates sparks that may
cause fire. Do not use the machine near
ignitable substances or gases.