WORKING TECHNIQUES
26 – English
Working methods
• Before you start clearing, check the clearing area, the
type of terrain, the slope of the ground, whether there
are stones, hollows etc.
• Start at whichever end of the area is easiest, and clear
an open space from which to work.
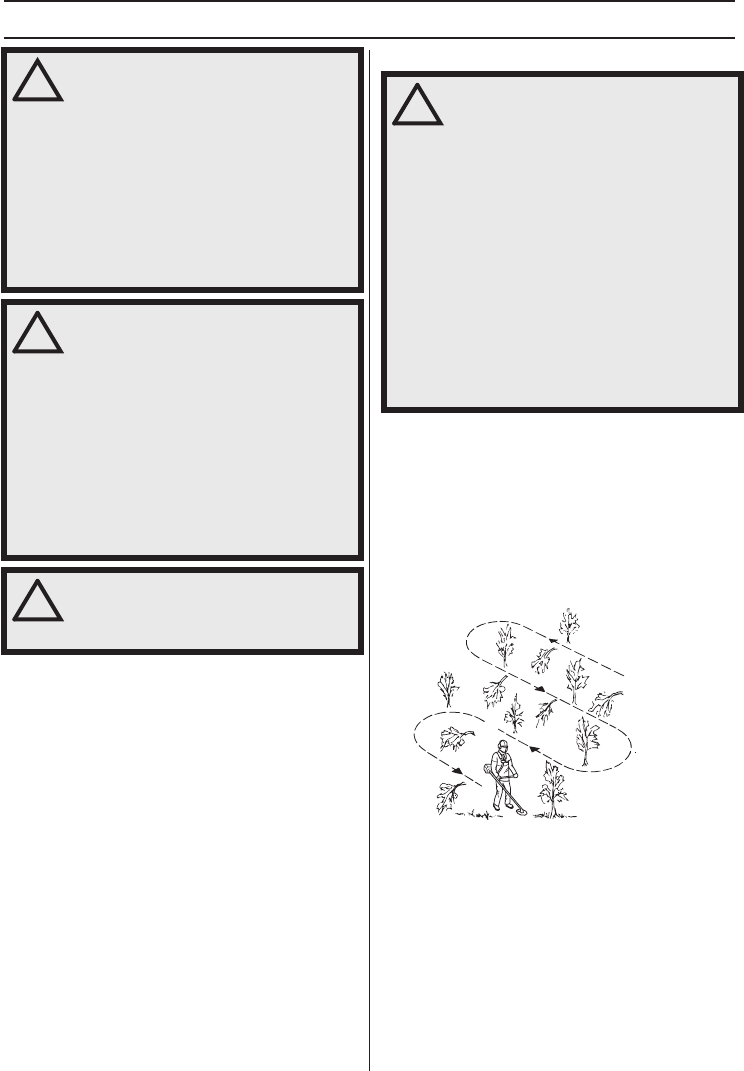
• Work systematically to and fro across the area,
clearing a width of around 4-5 m on each pass. This
exploits the full reach of the machine in both directions
and gives the operator a convenient and varied
working area to work in.
• Clear a strip around 75 m long. Move your fuel can as
work progresses.
• On sloping ground you should work along the slope. It
is much easier to work along a slope than it is to work
up and down it.
• You should plan the strip so that you avoid going over
ditches or other obstacles on the ground. You should
also orient the strip to take advantage of wind
!
WARNING! Neither the operator of the
machine nor anyone else may attempt to
remove the cut material while the engine
is running or the cutting equipment is
rotating, as this can result in serious
injury.
Stop the engine and cutting equipment
before you remove material that has
wound around the blade shaft as
otherwise there is a risk of injury. The
bevel gear can get hot during use and
may remain so for a while afterwards. You
could get burnt if you touch it.
!
WARNING! Watch out for thrown objects.
Always wear approved eye protection.
Never lean over the cutting attachment
guard. Stones, rubbish, etc. can be
thrown up into the eyes causing
blindness or serious injury.
Keep unauthorised persons at a
distance. Children, animals, onlookers
and helpers should be kept outside the
safety zone of 15 m. Stop the machine
immediately if anyone approaches. Never
swing the machine around without first
checking behind you to make sure no-
one is within the safety zone.
!
WARNING! Sometimes branches or
grass get caught between the guard and
cutting attachment. Always stop the
engine before cleaning.
!
WARNING! Machines fitted with saw
blades or grass blades can be thrown
violently to the side when the blade
comes into contact with a fixed object.
This is called blade thrust. A blade thrust
can be violent enough to cause the
machine and/or operator to be propelled
in any direction, and possibly lose
control of the machine. Blade thrust can
occur without warning if the machine
snags, stalls or binds. Blade thrust is
more likely to occur in areas where it is
difficult to see the material being cut.
Avoid cutting with the area of the blade
between the 12 o'clock and 3 o'clock
positions. Because of the speed of
rotation of the blade, blade thrust can
occur if you attempt to cut thick stems
with this area of the blade.