23
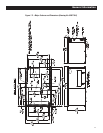
Figure 2.3 – Typical Generator Restraint
2.2 GENERATOR COMPARTMENTS
Whether the generator set is being installed inside a compartment
specifically manufactured to house a generator or inside a com-
partment that the installer constructs, the compartment must meet
certain specifications as outlined in the following sections:
2.2.1 COMPARTMENT SIZE
Plan the compartment size carefully. Provide a minimum clearance
of 1/2 inch (13 mm) on the front and top, one (1) inch (25 mm) on
the sides, and one (1) inch (25 mm) from the back for air circula-
tion AFTER the compartment has been lined with metal and sound
insulation (Figure 2.4).
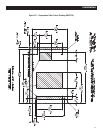
Figure 2.4 – Clearances
1" Clearance
in Back
1/2" Clearance on Top
1" Each Side
1/2"
in Front
Insulation
Plywood
Compartment
18" Clearance Recommended
Below (Minimum 12")
NOTE:
Refer to “Figure 1.2 – Major Features and Dimensions”.
2.2.2 COMPARTMENT CONSTRUCTION
The generator compartment should be either constructed of, or •
lined with, 26-gauge galvanized steel.
NOTE:
Aluminum is NOT an acceptable alternative to galvanized steel
due to aluminum’s low melting point.
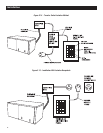
If the compartment is lined with galvanized steel, it may be •
constructed of any material. The manufacturer recommends
that the compartment be constructed of 1/2-inch thick plywood
(not strandboard), with the floor made of a double thickness of
1/2-inch plywood with the grain of the wood at cross section
for added strength (Figure 2.5).
Figure 2.5 – Typical Compartment Construction
If constructing a compartment, line the exterior (underside) of •
the compartment floor with 26-gauge galvanized steel.
All seams, splices and joints of the compartment walls (unless •
vapor tight by design) should be caulked to prevent poison-
ous, flammable or explosive vapors from entering the vehicle
interior.
NOTE:
Caulking must be done so that the caulking material will stay in
place permanently. Pressing such materials as putty tape onto
joints and seams is NOT acceptable. A high quality silicone rubber
base sealant is recommended.
Holes and openings made in the compartment walls to allow for •
the passage of electrical conduit, conductors, hoses, cables,
etc., into the vehicle living area must be sealed vapor tight with
silicone rubber base sealant.
If flexible metal conduit is used, it must be sealed internally at •
the end where it terminates inside the compartment’s electrical
junction box.
NOTE:
Flexible metal conduit, due to its unique construction, is NOT
vapor tight along its entire length.
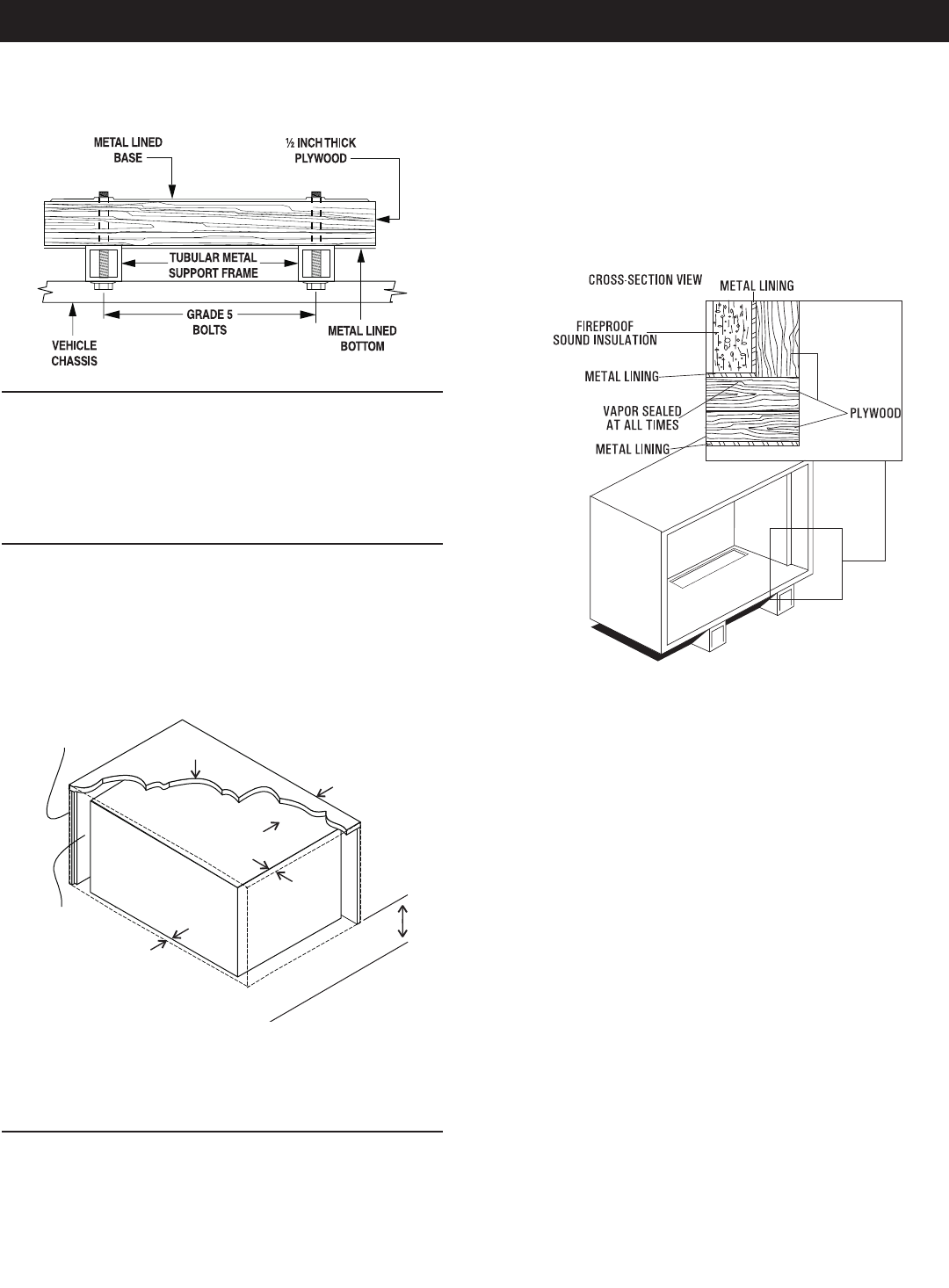
Seams and joints of the galvanized steel (whether used as a liner •
or for the compartment itself) must be lapped and mechanically
secured. Such seams may be manufactured, welded, bolted,
riveted or screwed. Manufactured lock seams are shown in
Figure 2.6. Installer constructed compartments typically utilize
a standard lap joint.
Installation