21
Chapter 6: Setting Up and Configuring the Router
How to Access the Web-based Utility
Wireless-N Gigabit Security Router with VPN
How to Access the Web-based Utility
There are two ways to connect to your Wireless Router for the first time.
1. Connect your PC to one of the four LAN ports on the Router. (Refer to "Chapter 5: Connecting the Router.")
Then, configure your PC to obtain IP address automatically through a DHCP server.
2. Although it is not recommended, you can also connect your PC wirelessly to the Wireless Router. Then,
configure the wireless interface of your PC to obtain IP address automatically through a DHCP server. It is not
recommended, because you can easily lose your connection through wireless configuration changes.
To access the Web-based Utility of the Router:
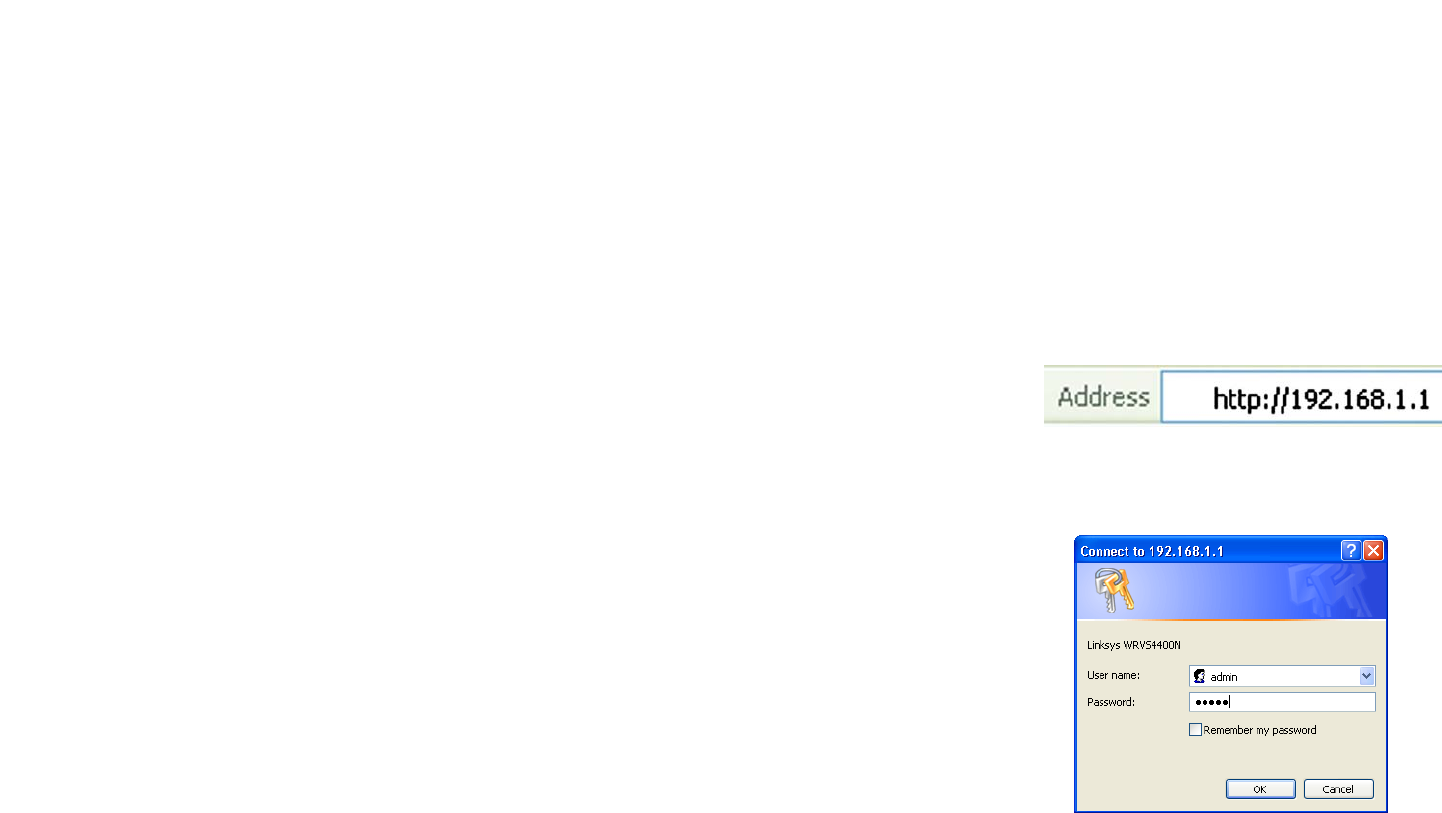
• Launch a web browser, such as Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox, and enter the Router’s default IP address,
192.168.1.1, in the Address field. Press the Enter key.
• A screen will appear asking you for your User name and Password. Enter admin in the User Name field, and
enter your password (default password is admin) in the Password field. Then click the OK button.
How to Navigate the Utility
The Web-based Utility consists of the following nine main tabs: Setup, Wireless, Firewall, VPN, QoS,
Administration, IPS, L2 Switch and Status. Additional screens (sub tabs) will be available from most of the main
tabs.
The following briefly describes the main & sub tabs of the Utility.
Setup
You will use the Setup tabs to define the Router’s basic functionality.
• IP Version. This screen provides options for IPv4 mode or Dual-Stack IPv4 and IPv6 mode.
• WAN. The Internet connection settings are entered and displayed on this screen.
• LAN. The Local Area Network (LAN) settings are entered and displayed on this screen.
• DMZ. The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) Host feature allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet to use a
special-purpose service such as Internet gaming or video conferencing.
Figure 6-1: Router’s IP Address
Figure 6-2: Login Screen for Web-based
Utility
