48
G Wireless Router
SECTIONSTable of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 106
UsingtheWeb-basedadvancedUserinterface
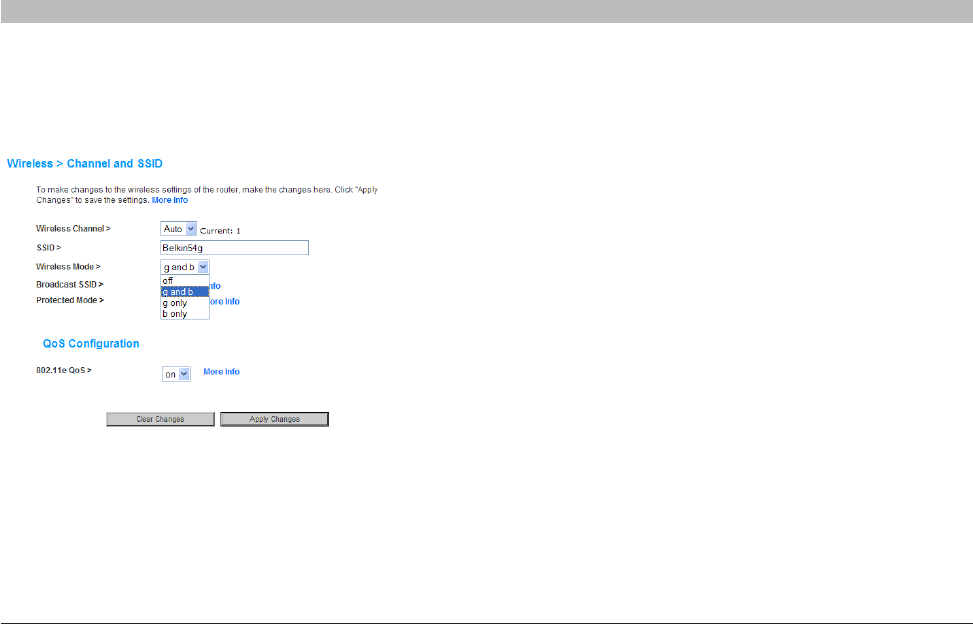
Using the Wireless Mode Switch
Your Router can operate in four different wireless modes: “g and b”, “g
only”, “b only”, and “off”. The different modes are explained (below).
g and b Mode
In this mode, the Router is compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g wireless
clients simultaneously. This is the factory default mode and ensures
successful operation with all Wi-Fi-compatible devices. If you have a mix
of 802.11b and 802.11g clients in your network, we recommend setting the
Router to g and b mode. This setting should only be changed if you have a
specific reason to do so.
g only Mode
802.11g mode works with 802.11g clients only. This mode is
recommended only if you want to prevent 802.11b clients from accessing
your network. To switch modes, select the desired mode from the
“Wireless Mode” drop-down box. Then, click “Apply Changes”.
b only Mode
We recommend you DO NOT use this mode unless you have a very
specific reason to do so. This mode exists only to solve unique problems
that may occur with some 802.11b client adapters and is NOT necessary
for interoperability of 802.11g and 802.11b standards.
off Mode
This option will turn off the wireless functionality.
When to use b only Mode
In some cases, older 802.11b clients may not be compatible with
802.11g wireless. These adapters tend to be of inferior design and
may use older drivers or technology. Switching to this mode can solve
problems that sometimes occur with these clients. If you suspect that
you are using a client adapter that falls into this category of adapters,
first check with the adapter vendor to see if there is a driver update. If
there is no driver update available, switching to b only mode may fix your
problem. Please note that switching to b only mode will decrease
802.11g performance.
