10
simulates a short to ground and pops the breaker. This turns off the outlets.
Pressing the RESET button allows the outlets to turn on and provide power.
Use with Appliances
Make sure the AC appliance can operate on 110/120 Volts, 60 Hz AC
modified sine wave (MSW) as most appliances sold in the USA can. There are
a few exceptions, noted later.
• Plug the appliance’s two or three-pin North American standard plug into
the GFCI AC receptacle on the inverter
• Turn On the inverter’s power switch
• Turn On the appliance and operate it as usual
• After use, turn Off the power inverter’s On/Off Switch
5.2 Principles of Operation
The Power Inverter converts power in two stages. The first stage is a DC-to-DC
conversion process that raises the low voltage DC at the inverter input to 145
Volts DC. The second stage is the actual inverter stage that converts the high
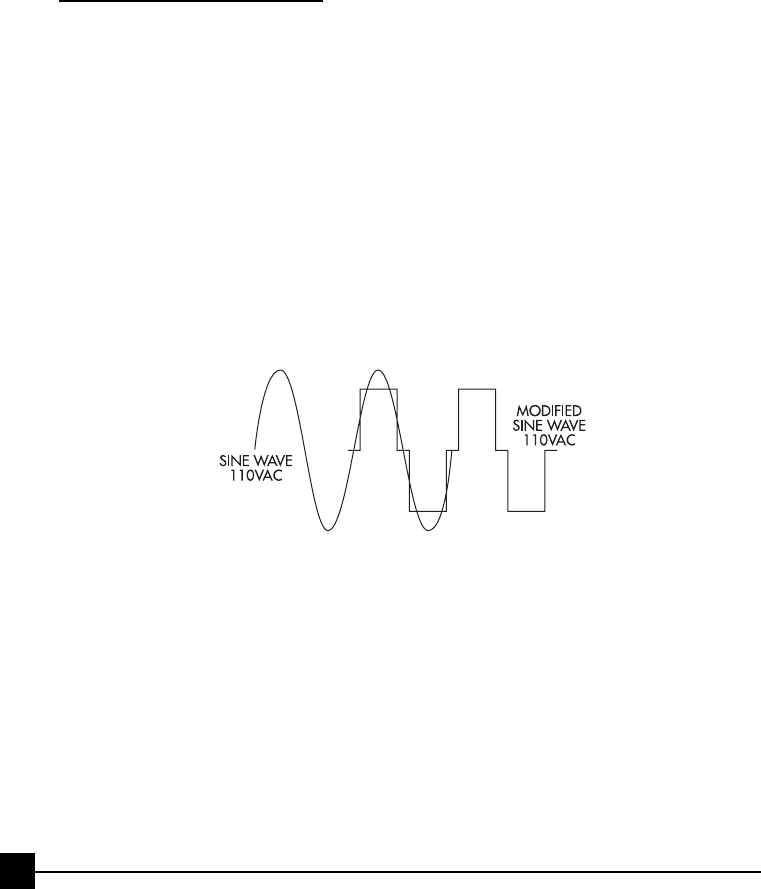
voltage DC into 110 Volts, 60 Hz AC, Modified Sine Wave (MSW). MSW is a
waveform that has characteristics similar to the sine wave shape of utility
power. This type of waveform is suitable for most AC loads, including linear
and switching power supplies used in electronic equipment, transformers, and
motors. The modified sine wave produced by the Power Inverter has an RMS
(root mean square) voltage of 110, which is the same as standard household
power. Most AC voltmeters (both digital and analog) are calibrated for RMS
voltage under the assumption that the waveform measured will be a pure sine
wave. These meters will NOT READ the RMS voltage of a modified sine wave
correctly. They will read about 20 to 30 Volts low when measuring the output
of the power inverter. For accurate measurement of the output voltage of this
unit, use a voltmeter marked “TRUE RMS”. Figure 6 compares a Modified Sine
Wave with a True Sine Wave.
FIGURE 6
Power is provided to the inverter through two conductors that pass through the
battery compartment cover. With a full charge on the battery (typically 85AH),
the inverter will supply an AC load of 100 watts for approximately 8 hours.
Lower wattage loads will operate longer, higher wattage loads will operate
for a shorter time.
Example: If a load is rated at 100 watts AC, the power source must be able to
deliver: 100 / 10 = 10 amperes
CAUTION: The inverter must be connected only to batteries with a nominal
output voltage of 12 Volts. The unit will not operate from a 6 volt battery and
will sustain permanent damage if connected to a 24 VOLT battery.
WARNING: NEVER TRY TO JUMPSTART A 6 OR 24 VOLT SYSTEM.
DAMAGE TO THE INVERTER AND INTERNAL BATTERY CAN RESULT.


















