Dayton Operating Instructions and Parts Manual
10
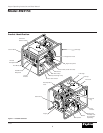
Dayton Diesel Electric Generator
®
4W315C
107358
IMPORTANT: This generator will not
power your entire home. Most home
utility electric service is more than 60
amps. This will exceed generator output.
Only power needed items during a power
outage. Make sure total wattage of
electrical load does not exceed rated
wattage of generator.
You can use this generator as a standby
power source. During a power outage, the
generator will power selected items in a
building. Have generator and additional
wiring installed by a skilled, licensed
electrician. This is not a do-it-yourself job.
Follow all local codes.
The electrician must install a double-
throw transfer switch. This isolates
existing electrical circuits from the
utility power line. If not isolated,
generator output
will back-feed into
utility power line.
This may electrocute a power company
line repair person.
EXTENSION CORDS
Only use grounded extension cords. Be sure
to use extension cord with proper wire
gauge size. See chart below.
RECOMMENDED MINIMUM WIRE
GAUGES (AWG) FOR EXTENSION CORDS
Ampere AWG for AWG for AWG for
Load 50' Cord 100' Cord 150' Cord
218 18 18
318 18 18
416 16 16
516 16 16
616 16 14
816 14 12
10 16 14 12
12 14 14 12
14 14 12 10
16 12 12 10
20 10 10 8
GROUND FAULT PROTECTION
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
helps guard against electric shock. On
construction sites, you must use a GFCI.
OSHA and the National Electric Code
requires this.
2. Enter running watts of each item except
motors. The light bulb or appliance
nameplate lists its wattage. Remember,
1KW = 1000 watts.
NOTE: The nameplate may not list
wattage. It may only list volts and amps.
The formula for finding wattage is: Volts x
Amps = Watts. For example: An appliance
nameplate states 3 amps at 120 volts. 3
amps x 120 volts = 360 watts.
3. Electric motors present a special
problem. They require 3 to 6 times their
rated full-load wattage to start. Chart 2,
page 11, shows starting watts (maxi-
mum volt-amperes [VA]) for different
size motors. For example: an electric
motor nameplate states 5 amps at 120
volts. 5 amps x 120 volts = 600 watts
running. Multiply this figure by 3. This
will show the starting watts (maximum
VA) needed. 600 watts x 3 = 1800
watts (VA) to start. When figuring the
generator load for motors, you must use
the starting watts (maximum VA) figure.
Do not use the running watts figure.
NOTE: Some motors require nearly the
same wattage to run as to start. These
items include saws, drills, hair dryers, and
food mixers. See Chart 1, page 11 for
typical appliance wattage examples.
4. Add watts and starting watts (maximum
VA) of all items. This total must not be
larger than 5000 watts. It is a good idea
to have up to 25% extra capacity for
future needs or extra equipment.
dust, dirt, rain, or snow to collect on it.
Protect generator from outdoor elements.
Installation (Continued)
DETERMINING ELECTRICAL LOAD FOR
GENERATOR
You must decide what electrical load your
generator can power. Do this before using
generator. Use the following four-step
method. It will help you select a load that
is not too large. Make sure total wattage
of all electrical loads does not exceed
5000 watts. Electric motors present a
special problem when figuring load. Read
Step 3 carefully.
1. Make two lists of items you want
powered by generator. List all motors
and motor powered appliances in one.
List all lights, small appliances, etc. in
the other. For standby service to home
or building, only include items you must
power.
STANDBY INSTALLATION TO HOME OR
BUILDING
Have standby
installation
performed by a skilled, licensed
electrician. Do not let anyone else wire
into a utility circuit. Personal injury,
equipment damage, or damage to
home could occur.