6
LOAD APPLICATION
It is important to determine the total electrical load
before it is connected to the generator. The two major
factors in determining the life of a generator head are:
heat build-up, caused by overloading the generator
and corrosive contaminants that attack the wiring
insulation. If the generator is overloaded, the wires
become excessively hot and cause the insulation to
break down, reducing its ability to resist corrosive
contaminants. Over time the effectiveness of the
insulation is eliminated and a dead short can result.
Always compare the generator nameplate data
with that of the equipment to be used to ensure that
watts, volts, amperage, and frequency requirements
are suitable for operating equipment. The wattage
listed on the equipment nameplate is its rated output.
However, some equipment may require three to ten
times more wattage than its rating on the nameplate,
as the wattage is influenced by the equipment
efficiency, power factor and starting system. NOTE: If
wattage is not given on equipment nameplate,
approximate wattage may be determined by
multiplying nameplate voltage by nameplate
amperage.
VOLTS X AMPS = WATTS
Example: 120V X 5A = 600W
When connecting a resistive load such as
incandescent lights, heaters or common electric power
tools, a capacity of up to the generator full rated
wattage output can be used.
When connecting a resistive-inductive load such
as a fluorescent or mercury light, transformers or
inductive coils, a capacity of up to 0.6 times the
generator full rated output can be used.
Always allow the generator to reach operating
speed before a load is applied.
STARTING ELECTRIC MOTORS
Electric motors require much more current (amps)
to start than to run. Some motors, particularly low cost
split-phase motors, are very hard to start and require 5
to 7 times more current to start than to run. Capacitor
motors are easier to start and usually require 2 to 4
times as much current to start than to run. Repulsion
Induction motors are the easiest to start and require
1.5 to 2.5 times as much to start than to run.
Most fractional motors take about the same
amount of current to run them whether they are of
Repulsion-Induction (RI), Capacitor (Cap), or Split-
Phase (SP) type. The following chart shows the
approximate current required to start and run various
types and sizes of 120 volt 60 cycle electric motors
under various conditions.
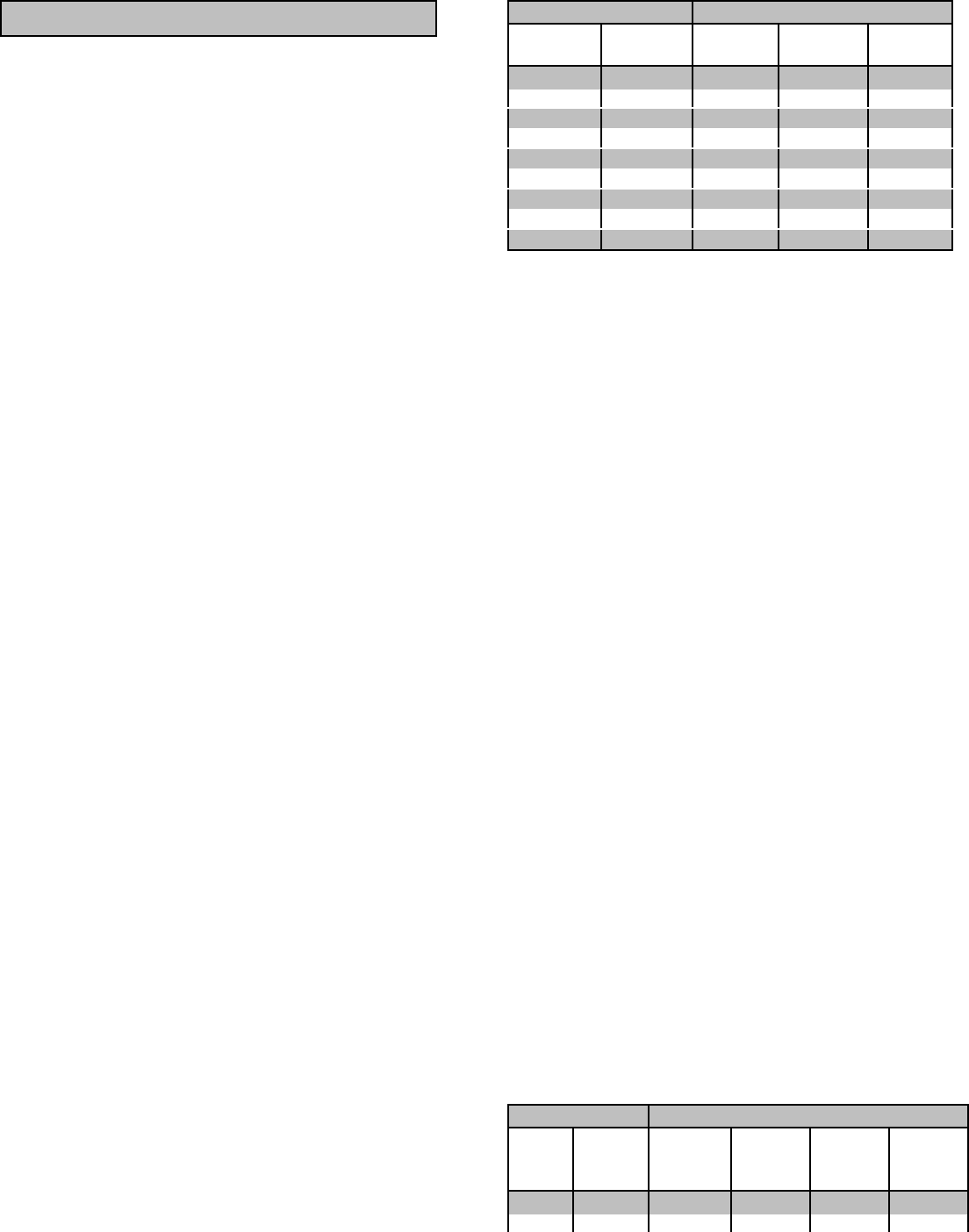
120V, 60 Hz Motors
Starting Amps
Hp motor Running
Watts
RI type Cap type SP type
1/6 525 7-11 9-18 16-22
1/4 700 9-15 12-23 22-32
1/3 875 11-18 14-29 26-35
1/2 1175 15-25 20-40 NA
1 1925 24-40 32-64 NA
1 1/2 2400 30-50 40-80 NA
2 2900 36-60 48-96 NA
3 4075 51-85 68-136 NA
5 6750 84-140 112-224 NA
The figures given above are for an average load
such as a blower or fan. If the electric motor is
connected to a hard starting load such as an air
compressor, it will require more starting current. If it is
connected to a light load or no load such as a power
saw, it will require less starting current. The exact
requirement will also vary with the brand or design of
the motor.
Generators respond to severe overloading
differently than the power line. When overloaded, the
engine is not able to supply enough power to bring the
electric motor up to operating speed. The generator
responds to the high initial starting current, but the
engine speed drops sharply. The overload may stall
the engine. If allowed to operate at very low speeds,
the electric motor starting winding will burn out in a
short time. The generator head winding might also be
damaged.
Running the generator under these conditions may
result in damage to the generator stator as well as the
motor windings. Because the heavy surge of current
is required for only an instant, the generator will not be
damaged if it can bring the motor up to speed in a few
seconds. If difficulties in starting a motor are
experienced, turn off all other electrical loads and if
possible reduce the load on the electric motor.
EXTENSION CORDS
When electric power is to be provided to various
loads at some distance from the generator, extension
cords can be used. These cords should be sized to
allow for distance in length and amperage so that the
voltage drop between the set and point of use is held
to a minimum.
Current/Power Maximum Extension Cord Length
Amps
at
240V
Load
(watts)
#10
Ga.
Cord
#12
Ga.
Cord
#14
Ga.
Cord
#16
Ga.
Cord
10 2400 250’ 150’ 100’ 75’
20 4800 125’ 75’ 50’ 25’












