6 MHD56391 - Edition 2
Load Chain Reports
Records should be maintained documenting the condition of load
chain removed from service as part of a long-range load chain
inspection program. Accurate records will establish a relationship
between visual observations noted during frequent inspections and
the actual condition of the load chain as determined by periodic
inspection methods.
Frequent Inspection
Manual Chain Hoists should be inspected at the beginning of each
shift. Visual inspections should also be conducted during regular
service for any damage or evidence of malfunction which appears
between regular inspections.
1. Operation. Check for visual signs or abnormal noises which
could indicate a potential problem. Do not operate a hoist
unless the load chain feeds through the hoist and hook block
smoothly. Listen for “clicking”, binding or malfunctioning.
The clicking sound of the pawl on the ratchet gear is normal
when a load is being raised. If chain binds, jumps, or is
excessively noisy, clean and lubricate the chain. If problem
persists, the chain and load sheave may have to be replaced.
Do not operate the hoist until all problems have been
corrected. Check that hand chain moves freely without
binding or excessive drag. Load chain travel should stop
when hand chain stops moving.
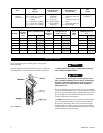
2. Hooks. Check for wear or damage, increased throat width,
bent shank or twisting of hook. Replace hooks which exceed
the throat opening discard width (15%) shown in Table 1
(refer to Dwg. MHP0040 on page 6) or exceed a 10° twist
(refer to Dwg. MHP0111 on page 6). If the hook latch snaps
past the tip of the hook, the hook is sprung and must be
replaced. Check hooks swivel easily and smoothly. Repair or
lubricate as necessary.
(Dwg. MHP0111)
(Dwg. MHP0040)
Table 1: Hook Throat Opening
Model No.
Normal Discard
in
mm in mm
SMB005 0.94
24 1.09 27.6
SMB010 1.00
26 1.18 30
SMB015
1.10 33 1.50 38
SMB020
SMB030 1.50 39 1.76 44.8
SMB050 1.89
48 2.17 55.2
3. Hook Latches. Check operation of the hook latches. Replace
if broken or missing.
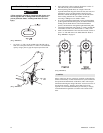
4. Chain. Refer to Dwg. MHP0102 on page 6. Examine each
link for bending, cracks in weld areas or shoulders, transverse
nicks and gouges, weld splatter, corrosion pits, striation
(minute parallel lines) and chain wear, including bearing
surfaces between chain links. Replace a chain that fails any
of the inspections. Check lubrication and lubricate if
necessary. Refer to “Load Chain” in “LUBRICATION”
section
on page 7.
(Dwg. MHP0102)
CAUTION
• The full extent of chain wear cannot be determined by visual
inspection. At any indication of chain wear, inspect chain and
load sheave in accordance with instructions in “Periodic
Inspection.”
• A worn load chain may cause damage to the load sheave.
Inspect the load sheave and replace if damaged or worn.
5. Load Chain Reeving. Refer to Dwg. MHP0042 on page 9.
Make sure welds on standing links are away from load
sheave. Reinstall chain if necessary. Check that the last link
of the load chain is securely connected. On 2, 3 and 5 ton
hoists, make sure chain is not capsized, twisted or kinked.
Adjust as required.
Periodic Inspection
According to ASME B30.16, frequency of periodic inspection
depends on the severity of usage:
NORMAL HEAVY SEVERE
yearly semiannually quarterly
Disassembly may be required for HEAVY or SEVERE usage.
Keep accumulative written records of periodic inspections to
provide a basis for continuing evaluation. Inspect all items in
“Frequent Inspection”. Also inspect the following: