26
USING THE DIFFERENTIAL LOCK
Depressing the differential lock pedal engages a
mechanism in the transmission that locks the
differential. This prevents the rear wheels from
rotating independently of each other and provides
constant power to both rear wheels when additional
traction is needed.
IMPORTANT:
Do not engage the differential
lock when one of the rear wheels is rotating. Stop
the wheel rotation and then engage the
differential lock.
WARNING: When operating with the dif-
ferential lock engaged, the tractor will be
difficult to steer. Do not drive the tractor
on roadways or at high speeds with the
differential lock engaged.
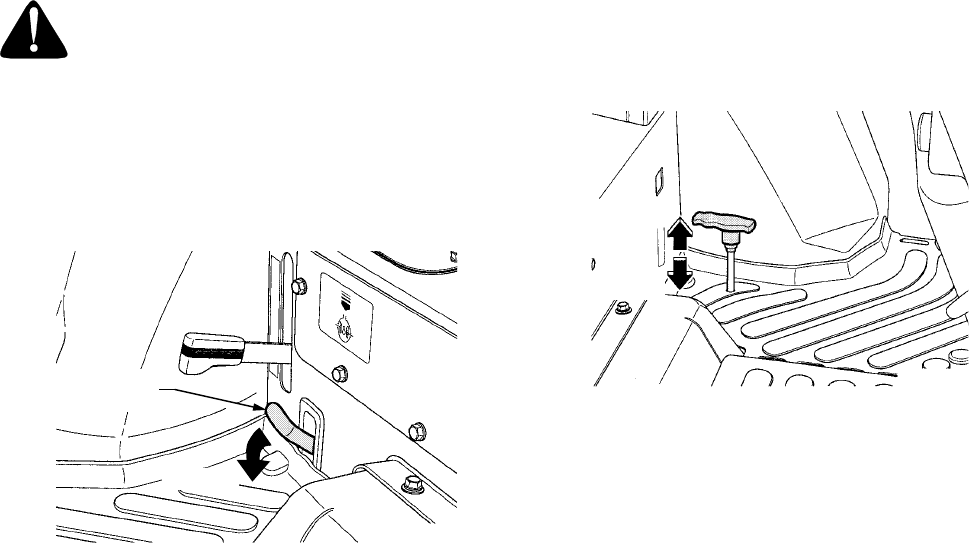
• Using your heel, fully depress and hold the
differential lock pedal to engage the transmission
differential lock. Release the pedal to disengage
the differential lock. See Figure 30.
Figure 30
• Apply the differential lock moderately. Limit its
use to situations where the tractor is stopped or is
unable to drive straight because one its rear
wheels has lost traction due to slippery or loose
soil.
• Do not engage the differential lock for prolonged
periods. Release the pedal when traction has
been restored.
NOTE: Because of the drive load on the internal
engagement mechanism, releasing the pedal may not
always disengage the differential lock even though
the pedal springs back. It may be necessary to slow
the tractor, or engage the brake pedal, to disengage
the differential lock.
USING THE FRONT WHEEL DRIVE
Use the front wheel drive when the conditions require
the additional traction provided by all four wheels
driving the tractor.
For example:
• When operating ground engaging equipment,
such as a front end loader, that may cause the
rear wheels to break traction.
• When climbing slopes.
• When operating in wet, sandy or loose soil
conditions.
To engage the front wheel drive mechanism, depress
the clutch pedal, stop the tractor, and push the front
wheel drive lever downward. See Figure 31.
Figure 31
To disengage the front wheel drive, depress the
clutch pedal and pull the lever upward.
USING THE POSITION CONTROL AND DRAFT
CONTROL LEVERS
• Use the position control lever to set the height of
a 3-point hitch mounted implement if drag on the
tractor is not a concern.
• Set the draft control lever to control the drag on
the tractor when operating a 3-point hitch
mounted implement. Draft control will maintain a
constant drag on the tractor by continually raising
and lowering the implement as different soil
conditions are experienced.
• Use a combination of the two levers to set the
height of the implement while also controlling the
drag on the tractor. Refer to Figure 32.
Engage
DIFFERENTIAL
LOCK PEDAL
Engage
Disengage


















