SERVICING
70
4. Two-Stage Condensing Unit: The maximum length of
tubing must not exceed 80 feet where indoor coil is
located above the outdoor unit.
NOTE: When the outdoor unit is located above the
indoor coil, the maximum vertical rise must not exceed
25 feet. If the maximum vertical rise exceeds 25 feet,
premature compressor failure will occur due to inad-
equate oil return.
5. Most refrigerant tubing kits are supplied with 3/8"-
thick insulation on the vapor line. For long line
installations over 80 feet that pass through a high
ambient temperature, ½”-thick suction line insula-
tion is recommended to reduce loss of capacity.
Insulate the liquid line if it passes through an area
of 120°F or greater. Do not attach the liquid line to
any non-insulated portion of the suction line.
6. Vibration and Noise: In long line applications, refriger-
ant tubing is highly prone to transmit noise and vibration
to the structure it is fastened to. Use adequate vibration-
isolating hardware when mounting line set to adjacent
structure.
Table 4 lists multiplier values to recalculate system-cooling
capacity as a function of a system’s equivalent line length (as
calculated from the suction line) and the selected suction
tube size. Table 5 lists the equivalent length gained from
adding bends to the suction line. Properly size the suction
line to minimize capacity loss.
TABLE 4. CAPACITY MULTIPLIERS AS A FUNCTION OF
SUCTION LINE SIZE & EQUIVALENT LENGTH
50
75
100
125
150
18,000
3/4
.99 .97 .96 .95 .95
24,000
3/4
1 .99 .99 .98 .97
30,000
3/4
.98 .97 .96 .95 .94
3/4
.93 .90 .86 .83 .79
7/8
.98 .96 .94 .92 .90
3/4
.93 .90 .87 .83 .80
7/8
.97 .96 .94 .93 .92
1-1/8
1 1 .99 .99 .98
3/4
.90 .86 .82 .78 N/R
7/8
.96 .94 .93 .91 .89
1-1/8
1 1 .99 .99 .98
7/8
.93 .91 .89 .86 .84
1-1/8
.99 .98 .98 .97 .97
36,000
42,000
48,000
60,000
Nominal
capacity
Btuh
Vapor line
diameter
(in.)
EQUIVALENT LINE LENGTH (FT)
NOTE: For a condenser with a liquid valve tube connection
less than 3/8" diameter, use 3/8" liquid line tubing for a line
set greater than 25 feet.
TABLE 5. LOSSES FROM SUCTION LINE ELBOWS
(EQUIVALENT LENGTH, FT.)
3/4 7/8 1-1/8
90° short radius 1.7 2 2.3
90° long radius 1.5 1.7 1.6
45° 0.7 0.8 1
I.D. (in.)
Type of elbow fitting
Installation Requirements
1. In a completely horizontal installation with a long line set
where the evaporator is at the same altitude as (or
slightly below) the condenser, the line set should be
sloped towards the evaporator. This helps reduce
refrigerant migration to the condenser during a system’s
off-cycle.
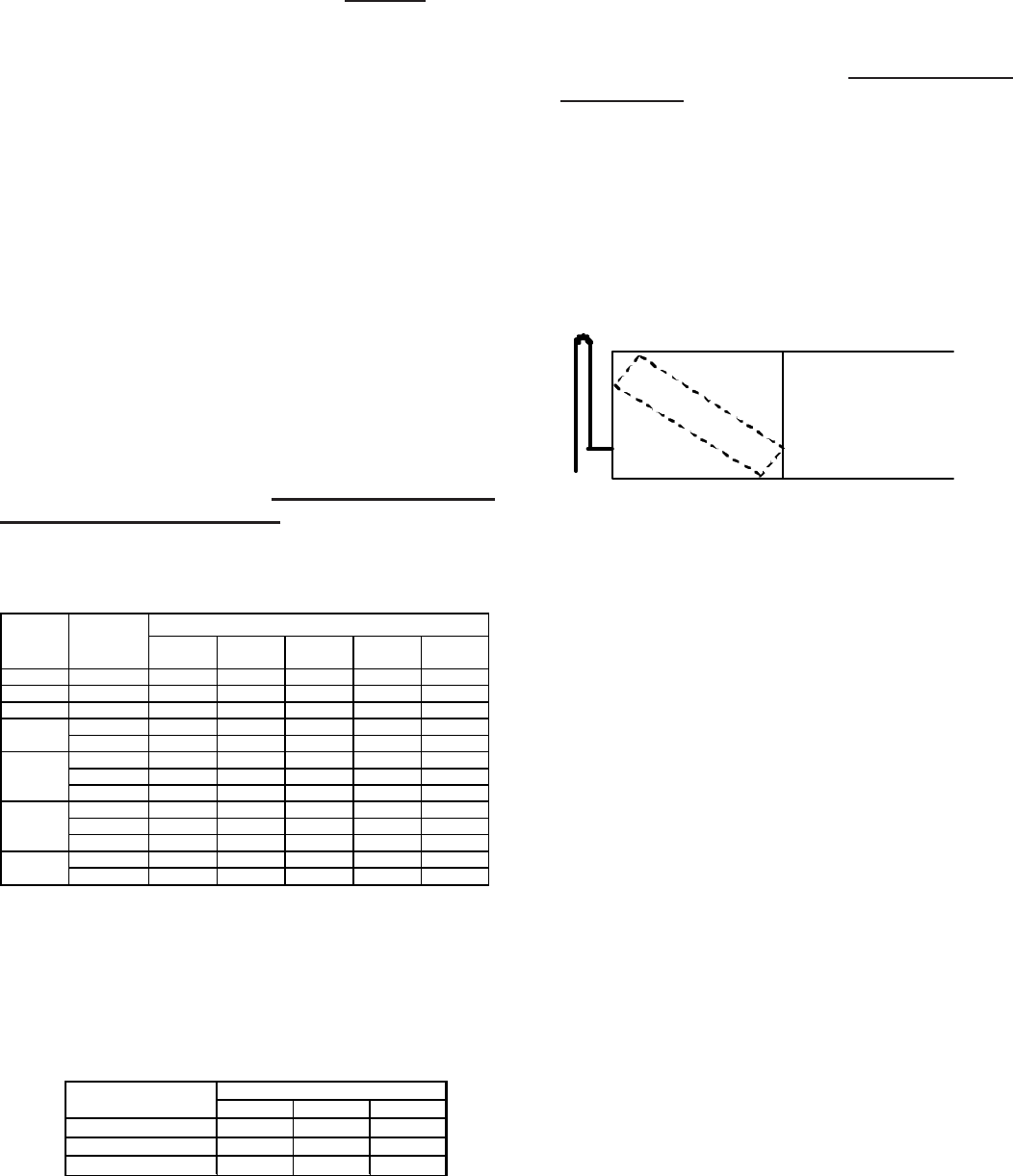
2. For a system installation where the
evaporator is above
the condenser, an inverted vapor line trap should be
installed on the suction line just before the inlet to the
evaporator (see Fig 6). The top of the inverted loop must
be slightly above the top of the evaporator coil and can
be created simply by brazing two 90° long radius elbows
together, if a bending tool is unavailable. Properly
support and secure the inverted loop to the nearest point
on the indoor unit or adjacent structure.
Fig 6. Evaporator unit with inverted vapor loop
3. An oil trap is required at the evaporator if the
condenser is above the evaporator. Depending on
the vertical rise of the line set, oil traps are required in the
suction line. Oil traps should be installed at equal
intervals along the suction line. Install 1 oil trap for a
height difference of 15–25 feet between indoor and
outdoor units. Install 2 oil traps for a difference of 26-50
ft, 3 for 51-100 ft, and 4 for 101-150 ft. Preformed oil traps
are available at most HVAC supply houses, or oil traps
may be created by brazing tubing elbows together (see
diagram below). Remember to add the equivalent length
from oil traps to the equivalent length calculation of the
suction line. For example, if you construct an oil trap
using two 45° elbows, one short and one long 90° elbow
in a ¾” diameter suction line, the additional equivalent
length would be 0.7+ 0.7+1.7+1.5, which equals 4.6 feet
(refer to Table 5).
