Cheetah 10K.7 SCSI Product Manual, Rev. D 51
8.4 Drive mounting
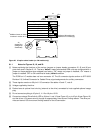
When mounting the drive using the bottom holes (x-y plane in Figure 15) care must be taken to ensure that the
drive is not physically distorted due to a stiff non-flat mounting surface. The allowable mounting surface
stiffness is 80 lb/in (14.0 N/mm). The following equation and paragraph define the allowable mounting surface
stiffness:
where ‘k’ represents the mounting surface stiffness (units of lb/in or N/mm), and ‘x’ represents the out-of-plane
mounting surface distortion (units of inches or millimeters). The out-of-plane distortion (‘x’) is determined by
defining a plane with three of the four mounting points fixed and evaluating the out-of-plane deflection of the
fourth mounting point when a known force (F) is applied to the fourth point.
Note. Before mounting the drive in any kind of 3.5-inch to 5.25-inch adapter frame, verify that the drive
can meet the shock and vibration specifications given herein while mounted in such an adapter
frame. Adapter frames that are available may not have a mechanical structure capable of mounting
the drive so that it can meet the shock and vibration specifications listed in this manual.
8.5 Grounding
Signal ground (PCBA) and HDA ground are connected together in the drive and cannot be separated by the
user. The equipment in which the drive is mounted is connected directly to the HDA and PCBA with no electri-
cally isolating shock mounts. If it is desired for the system chassis to not be connected to the HDA/PCBA
ground, the systems integrator or user must provide a nonconductive (electrically isolating) method of mount-
ing the drive in the host equipment.
Increased radiated emissions may result if you do not provide the maximum surface area ground connection
between system ground and drive ground. This is the system designer’s and integrator’s responsibility.
k * x = F < 15lb = 67N