40
www.ferrisindustries.com
Troubleshooting, Adjustment & Repair
BATTERY SERVICE
Checking Battery Voltage
A voltmeter can be used to determine condition of
battery. When engine is off, the voltmeter shows
battery voltage, which should be 12 volts. When
engine is running, the voltmeter shows voltage of
charging circuit which normally is 13 to 14 volts.
A dead battery or one too weak to start the engine
may not mean the battery needs to be replaced.
For example, it may mean that the alternator is not
charging the battery properly. If there is any doubt
about the cause of the problem, see your dealer. If
you need to replace the battery, follow the steps
under Cleaning the Battery & Cables in the Regular
Section.
Charging a Completely Discharged
Battery
1. Be aware of all the safety precautions you should
observe during the charging operation. If you are
unfamiliar with the use of a battery charger and
hydrometer, have the battery serviced by your
dealer.
2. Add distilled water sufficient to cover the plate (fill
to the proper level near the end of the charge).
If the battery is extremely cold, allow it to warm
before adding water because the water level will
rise as it warms. Also, an extremely cold battery
will not accept a normal charge until it becomes
warm.
3. Always unplug or turn the charger off before
attaching or removing the clamp connections.
4. Carefully attach the clamps to the battery in
proper polarity (usually red to [+] positive and
black to [-] negative).
5. While charging, periodically measure the
temperature of the electrolyte. If the temperature
exceeds 125° F (51.6° C), or if violent gassing or
spewing of electrolyte occurs, the charging rate
must be reduced or temporarily halted to prevent
battery damage.
WARNING
Keep open flames and sparks away from the
battery; the gasses coming from it are highly
explosive. Ventilate the battery well during
charging.
6. Charge the battery until fully charged (until the
specific gravity of the electrolyte is 1.250 or higher
and the electrolyte temperature is at least 60° F).
The best method of making certain a battery is
fully charged, but not over charged, is to measure
the specific gravity of a cell once per hour. The
battery is fully charged when the cells are gassing
freely at low charging rate and less than 0.003
change in specific gravity occurs over a three hour
period.
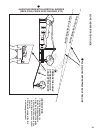
Jump Starting With Auxiliary (Booster)
Battery
Jump starting is not recommended. However, if it
must be done, follow these directions. Both booster
and dis-charged batteries should be treated carefully
when using jumper cables. Follow the steps below
EXACTLY, being careful not to cause sparks. Refer
to Figure 34.
1. Both batteries must be of the same voltage.
2. Position the vehicle with the booster battery
adjacent to the vehicle with the discharged battery
so that booster cables can be connected easily
to the batteries in both vehicles. Make certain
vehicles do not touch each other.
3. Wear safety glasses and shield eyes and face
from batteries at all times. Be sure vent caps are
tight. Place damp cloth over vent caps on both
batteries.
4. Connect positive (+) cable to positive post of
discharged battery (wired to starter or solenoid).
5. Connect the other end of same cable to same
post marked positive (+) on booster battery.
6. Connect the second cable negative (-) to other
post of booster battery.
7. Make final connection on engine block of stalled
vehicle away from battery. Do not lean over
batteries.
8. Start the engine of the vehicle with the booster
battery. Wait a few minutes, then attempt to start
the engine of the vehicle with the discharged
battery.
9. If the vehicle does not start after cranking for thirty
seconds, STOP PROCEDURE. More than thirty
seconds seldom starts the engine unless some
mechanical adjustment is made.
Not for
Reproduction