UNDERSTANDING THE CHEMISTRY
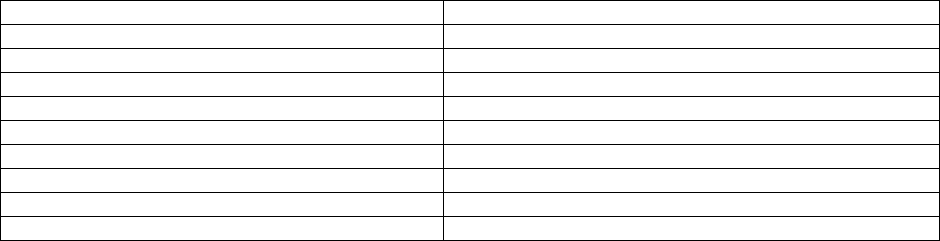
Below is a table showing the recommended balance levels followed by a more detailed explanation of the
factors affecting water chemistry. Maintaining these levels will prevent corrosion and scaling and will ensure
maximum enjoyment of the pool. You should test your water periodically. If the water chemistry needs
adjustment, your authorized dealer or most pool stores can supply you with the appropriate chemicals and
procedures. We recommend you either take a copy of the Water Balance Table to the pool store or notify the
pool store that you are using a salt chlorine generator.
FACTORS IDEAL LEVELS
Salt 3000 to 4000 ppm
Free Chlorine 1 to 3 ppm
PH 7.2 to 7.6
Total Alkalinity 110 to 180 ppm (Depending on the Saturation Index)
Stabilizer (Cyanuric Acid) 40-80 ppm
Nitrates 0 ppm
Metals 0 ppm
Phosphates O ppm
Calcium Hardness Determine level for individual pool surface
Saturation Index -0.3 to 0.3 (0 is ideal)
Salt
Salt is the power source of the Auto-Chlor Chlorine Generator. To ensure maximum benefits with the use of
the system, the ideal salt level is 4000 ppm (parts per million). A low concentration of salt can hinder the
generator’s effectiveness. A concentration of salt above 5500 ppm may cause corrosion damage to the pool
fixtures. See the Adding Salt section for more information.
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) are different from the salt level of the pool, although TDS levels rise by adding
salt to pool water. This does not harm the pool water chemistry or clarity, but the pool water professional that
is testing for TDS must be aware that salt has been added for the chlorine generator system. The pool
professional doing the TDS test will get the accurate TDS level by subtracting the salinity level.
Free Chlorine v. Combined Chlorine: The unpleasant smells and side effects often associated with chlorine
are actually caused by combined chlorine (i.e. chloramines). Combined chlorine is a chlorine molecule that
attacked a noxious particle in the water but has been unable to destroy that noxious particle. This chlorine
particle remains attached to the noxious particle until one of the two is burned off; hence the term “combined
chlorine” (a.k.a. chloramines). To burn off the noxious particle and free up the chlorine again, pool owners
have had to shock the pool periodically, but with the Auto-Chlor Chlorine Generator, the noxious particles are
burned off within the generator’s Cell and the combined chlorine is continuously converted back to free
chlorine.
The free chlorine level in the pool should be maintained at 1 to 3 ppm. This level of free chlorine is
comfortable to swim in with no unpleasant smells, and it maintains proper sanitizing power.
PH is a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. A scale of 0 to 14 is used to measure pH. Pure water
has a pH of 7 (neutral), acid solutions have a pH of less than 7, and basic (alkali) solutions have a pH of more
than 7. The recommended range is 7.2 to 7.8; chlorine is more effective within this range and the water is
most comfortable for bathers. Water with very high pH levels can cause scaling in the pool, on the walls and in
pipes. Low pH levels cause the water to be aggressive to the pool walls, equipment, and bathers.
To lower pH, add muriatic acid or dry acid, and to raise pH, add soda ash (sodium carbonate). Be sure to
read and follow the respective manufacturer’s instructions.
Total Alkalinity mitigates changes in pH. It is often referred to as the “big brother of pH.” Keeping proper
levels of total alkalinity will help reduce unwanted fluctuations in pH levels. Total alkalinity is also used to
offset high or low levels of calcium hardness (see Saturation Index below). Add muriatic acid or dry acid to
17